Table of Contents
Perfusion CT
Core vs Penumbra
| MTT | CBF | CBV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ |
| Penumbra | ↑ | ↓ | nl or ↓ |
Rapid AI
- CBF - cooler = worse
- CBF < 30% criteria
- MTT - hotter = worse
- Tmax > 6.0 seconds
- Report:
- Mismatch volume
- Mismatch ratio
Interpretation
- Start with TTP and delay images to spot abnormality
- MTT & CBF
- Then CBV to determine core vs penumbra
- Hypoperfusion index
- Volume of tissue with Tmax >10s/Tmax >6s
- Correlates with speed of growth of core infarct
- ≤0.3 is associated with better outcome
Reporting
- Sample
- Acute R MCA territory infarct with MCA/PCA penumbra.
- CBF < 30% of 17 mL, Tmax > 6 sec of 155 mL, and mismatch volume of 127 mL (ratio 8.5).
- Mismatch volume = salvageable penumbra
Terminology
- AIF = Arterial In-flow
- VOF = Venous Out-flow
- CBF = Cerebral Blood Flow
- core infarct
- overestimates infarct
- automated calculations
- CBV = Cerebral Blood Volume
- core infarct
- good for visual estimate
- Tmax = Arterial in-flow to capillary time
- ischemia
- MTT = Mean Transit Time = Capillary transit time
- ischemia
- least sensitive
- TTP = Time to Peak = Arterial in-flow to capillary time AND capillary transit time
- ischemia
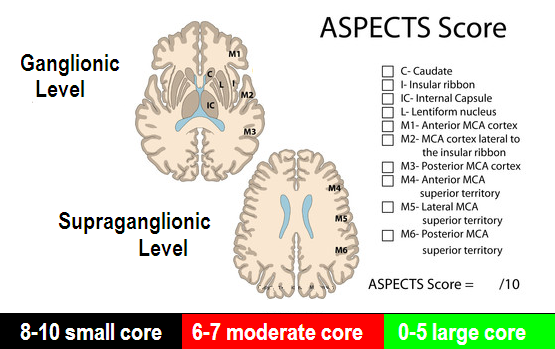
ASPECTS
- Areas with hemorrhage count as abnormal in aspects scoring.
- Dense MCA does not count.
- Other vascular territories do not count.
Posterior Circulation ASPECTS (pc-ASPECTS)
Microbleeds on MRI
- <5 - tPA safe
- >5 - safety unknown
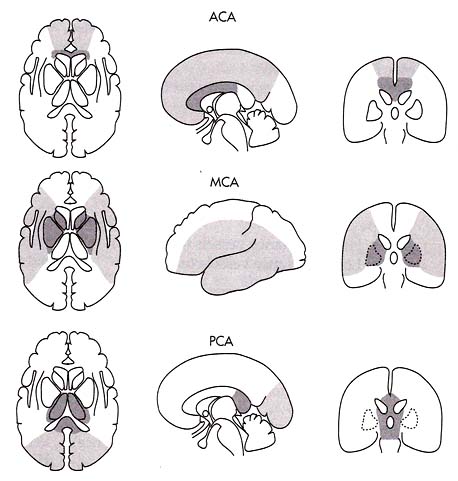
Vascular Anatomy
- MCA
- M1: sphenoidal or horizontal segment
- originates at the terminal bifurcation of the internal carotid artery
- courses laterally parallel to the sphenoid ridge
- terminates at one of two points (controversial; see below note*):
- at the genu adjacent to the limen insulae
- at the main bifurcation
- M2: insular segment
- originates at the genu/limen insulae or the main bifurcation (see above)
- courses posterosuperiorly in the insular cleft
- terminates at the circular sulcus of insula, where it makes a right angle to hairpin turn
- M3: opercular segment
- originates at the circular sulcus of the insula
- courses laterally along the frontoparietal operculum
- terminates at the external/superior surface of the Sylvian fissure
- M4: cortical segment
- originates at the external/top surface of the Sylvian fissure
- courses superiorly on the lateral convexity
- terminates at their final cortical territory
- The point where the M1 (sphenoidal) segment becomes the M2 (insular) segment is not agreed upon. As originally described by Fischer in 1938, the M1 segment ends where the artery turns 5. Although the bifurcation coincides with the genu in the classically described anatomy, most patients have a nonclassical bifurcation that occurs proximal or distal to the genu 6. Thus, the M1 could include rather than necessarily end at the main bifurcation. This landmark-based nomenclature was adopted in Gibo and Rhoton's microsurgical descriptions 7,8. In contrast, in the era of endovascular intervention, stroke expert groups have recommended the designation that the M1 ends at the main bifurcation 9,10. Different studies still variably define the M1-M2 distinction
- Recurrent artery of Heubner (aka medial lenticulostriate)
- branch of ACA
- caudate head, ant limb of internal capsule, septum pellucidum
- Lateral lenticulostriate
- branch of MCA
- lentiform nucleus, caudate capsule, internal capsule
- Thalamic and midbrain perforators
- branch of PCA
- SCA
- superior cerebellum
- AICA
- inferolateral pons
- middle cerebellar peduncle
- anterior cerebellum
- PICA
- medulla
- posterior and inferior cerebellum
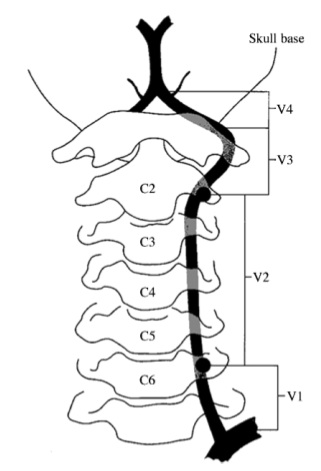
Vertebral Artery Anatomy
- Part one is from the origin to the point at which it enters the transverse foramina of either the fifth or sixth cervical vertebra.
- The second part courses within the intervertebral foramina
- The third part exits behind the atlas and heads towards the foramen magnum.
- The fourth part (intracranial) begins as it pierces thedura and arachnoid mater at the base of the skull, and ends as it meets its opposite vertebral artery to form the midline basilar artery at the level of the medullopontine junction.
White Matter Dz
Multiple Sclerosis Criteria
- 1 gad enh or 9 T2 hyper lesions
- 1+ infratentorial lesions
- 1+ juxtacortical
- 3+ periventricular
Multiple Sclerosis Variants
- Devic's dz - transverse myelitis & B optic neuritis
- severe
- Balo's dz - MS lesion w/ concentric demyelination & nl brain
- Schilder's dz - acute, rapid, B symmetric demyelination
- large, well-circ involving centrum & occ lobes
- Marburg variant - repeated relapses w/ rapidly accumulating disability
Multiple Sclerosis DDx
- Lyme
- vasculidities
- HTN & ischemic wm lesions
- virchow-robin spaces
- migraine
- trauma (DAI)
- UBO's
ADEM
- Causes - measles, varicella, mumps, rubella, EBV, CMV, M. pneumoniae
- multiple, large high T2 lesions which may enhance in a nodular or ring pattern
- usually affects cerebrum but may enlarge cord
- fulminant type is acute hemorrhagic leukoencephalitis (Hurst's dz)
- diffuse multifocal perivascular demylelination & hemmorhage in cerebral WM w/ sparing of U-fibers
PML
- JC virus
- assoc w/ immunocompromise
- asymmetric parietal & frontal involvement, but can be anywhere
- low T1, high T2
- no enhancement, no mass effect
HIV
- symmetric supratentorial demyelination
- does not extend to GW junction
- no mass effect
- atrophy
SSPE
- sequela of measles infection
- patchy WM demyelination sparing U-fibers
- asymmetric gray & white matter involvement in parietooccipital region
Binswanger dz
- older men & women
- assoc w/ HTN & lacunar infarction
- broad high signal areas w/i FPO WM
- U-fibers spared
CADASIL
- inherited arterial dz
- recurrent TIA, stroke, dementia, depression, pseudobulbar palsy, hemi/quadriplegia
- F/T/insula w/ subcortical U-fiber involvement
- High T2 in WM (periventricular, deep WM, BG, brain stem)
Postanoxic Encephalopathy
- occurs after anoxic episode severe enough to produce coma
- recovery after 24-48 hrs, then precipitous decline in 2-wk period to death
- high T2 throughout WM particularly involving corpus callosum, subcortical U-fibers, int/ext capsules
- diffusion positive
PRES
- high T2 in PO cortex & SCWM
- can extend to other regions
- enhancement variable
- does not restrict
- assoc w/
- malignant HTN
- toxemia of pregnancy
- renal dz
- immunosuppressive drugs (cyclosporine, FK-501)
- antiphospholipid ab syndrome
- porphyria
Central Pontine Myelinolysis
- alcoholic, debilitated, malnourished pt's w/ rapid correction of hyponatremia
- may involve extrapontine stx (thalamus, caudate, putamen, internal external & extreme capsules, claustrum, amygdala, cerebellum, deep gray matter)
- high T2 in pons w/ peripheral sparing and sparing of CST
Trauma
Extraaxial Hemorrhage
Epidural Hematoma
- Biconvex shape (lentiform)
- Usually in the temporoparietal regions but can be in the occipital region
- Usually accompanied with a skull fracture and tear of a branch of the middle meningeal artery
- Does NOT cross suture lines, but can cross midline
- Usually has more mass effect, but not always, depending on size
Subdural Hematoma
- Subdural is crescent shaped typically along the temporoparietal regions as well, and is associated with tearing of the bridging veins
- DO cross sutures lines, but DO NOT cross midline
- Fracture less commonly associated
- Can be bilateral and also interhemispheric, and along the tentorium.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- Subarachnoid you look for blood in the fissures, the basilar cisterns, interhemispheric, or in the interpeduncular fossa
- Blood in/around the circle of willis = star of texaco sign
- Blood along the posterior falx around the sinuses, you can get the delta sign
Vascular Lesions
- Approach to intraparenchymal hemorrhage
- If Ca2+ near hemorrhage think AVM
- Perform MR immediately (before blood products become bright on T1)
- If negative, f/u to resolution
- Approach to subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Obtain CTA while pt is on the table
- Non-aneurysmal SAH = Venous hemorrhage
- Perimesencephalic Cisterns
- Small amount of blood
- Asymptomatic
Berry Aneurysms
- Common Locations
- AComm (33%)
- PComm (33%)
- MCA Bifurcation (20%)
- Basilar Tip
Giant Aneurysms
- > 2.5 cm
- Common location is cavernous carotid
Spinal AVM
- Type 1
- dural AV fistula
- acquired lesion
- most common spinal AVM
- 1A - single feeding artery
- 1B - multiple feeding arteries
- nidus w/i or on dura of proximal nerve root sleeve in neural foramen
- progressive myelopathy & (rarely) SAH
- tx is surgical excision of nidus or endovascular glue
- Type 2
- glomus AVM
- intramedullary location
- compact nidus
- high-flow, produce flow-voids
- drainage into coronal venous plexus
- engorgement of post and/or anterior median vein
- perimedullary flow voids
- cord scalloping
- serpentine enhancement
- may cause enhancement in distant locations in cord
- Type 3
- Juvenile-type AVM
- more diffuse
- less prone to hemorrhage
- adolescents & young adults
- poorer prognosis, not amenable to surg excision
- typically cervical region
- can involve extramedullary, extradural, and extraspinal structures
- multiple arterial feeders, often from several different levels
- Type 4
- Perimedullary (conus/cauda equina) fistulas
- vary in severity
- 4A - slow flow, mod enlg veins, single feeding art
- tx surgically
- 4C - high flow, markedly dil veins, multiple feeders
- tx endovascularly
- progressive myelopathy, SAH (50%), acute paraplegia
Spaetzler Classification for AVM's
- Based on:
- Size
- Eloquence
- Drainage (deep vs superficial)
Chiari Malformations
Type I
- Tonsilar invagination through the foramen magnum into the spinal canal with variable degrees of tonsilar ectopia
- There is normal position of the 4th ventricle
- Syringohydromyelia is an associated finding
- Two components are necessary for the diagnosis - tonsilar herniation and syringohydromyelia
- May have associated basilar invagination, assimilation of C1 to the occiput, and Klippel-Feil
Type II
- Dysgenesis of the hindbrain with caudally displaced 4th ventricle and caudal elongation of the medulla and vermis
- Concurrent anomalies include: myelomeningocele, mesencephalic beaking (tectal beaking), enlarged massa intermedia, accessory anterior commissure, absence of the corpus callosum (which manifests as elevated third ventricle), partial absence of the falx, and cervicomedullary kinking
- Abnormalities of the bony vault include Luckenshadel (or lacunar) skull (appears as soap bubble lucencies in the upper calvaria)
- A dysplasia of bone and underlying dura
- Can be seen with any cause of meningocele and myelomeningocele
Type III
* A rare lesion that consists of herniation of cerebellum into a high cervical or occipital encephalocele
Type IV
* Consists of extreme cerebellar hypoplasia without associated displacement
Ischemia
Stroke
- Hyperacute (0-6 hrs)
- iso T1/T2
- high DWI/low ADC
- DWI may be positive within 2 hours
- Acute (6 hrs-4 days)
- low T1/high T2
- mass effect
- high DWI/low ADC
- Subacute (4-14 days)
- low T1/high T2
- resolving mass effect
- T2 shine through on diffusion
- pseudonormalization of ADC
- Chronic
- encephalomalacia
- high T2
- T2 shine through on diffusion
- high ADC
TPA Stroke Therapy
- IV w/i 3 hrs
- catheter directed w/i 6hrs
Wallenburg Syndrome
- Lateral medullary infarct
- affects CN 9,10
- causes hoarsness and dysphagia
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves
Facial Nerve Segments
- Cisternal segment
- The nerve emerges immediately beneath the pons, lateral to the abducens nerve and medial to the vestibulocochlear nerve, and is joined by the nervus intermedius which has emerged lateral to the main trunk. Together the two travel through the cerebellopontine angle to the internal acoustic meatus.
- Meatal (internal auditory canal) segment
- Having been joined by the nervus intermedius they are located in the superior upper quadrant, above the falciform crest and anterior to Bill's bar.
- Labyrinthine segment
- As the facial nerve and nervus intermedius pass through the anterior superior quadrant of the internal acoustic meatus it enters the Fallopian canal, passing anterolaterally between and superior to the cochlea (anterior) and vestibule (posterior), and then runs back posteriorly at the geniculate ganglion (where the nervus intermedius joins the facial nerve, and where fibers for taste synapse - see below). It is here that three branches originate: the greater superfical petrosal nerve, the lesser petrosal nerve and the external petrosal nerve. The labyrinthine segment is the shortest only measuring 3 to 4 mm. It is also the narrowest and the most susceptible to vascular compromise (see below).
- Geniculate ganglion
- Tympanic segment
- As the nerve passes posteriorly from the geniculate ganglion it becomes the tympanic segment (8-11 mm in length), and is immediately beneath the lateral semicircular canal in the medial wall of the middle ear cavity. The bone of the Fallopian canal is often dehiscent in the area of the oval window in 25-55% of postmortem specimens, having mucosa in direct contact with the nerve. The nerve pass posterior to the cochleariform process, tensor tympani and oval window. Just distal to the pyramidal eminence the nerve makes a second turn (second genu) passing vertically downwards as the mastoid segment. The tympanic segment has no branches.
- Mastoid segment
- The mastoid segment, measuring 8 to 14mm in length, extends from the second genu to the stylomastoid foramen, through what is confusingly referred to as the fallopian canal. It gives off three branches:
- nerve to stapedius
- chorda tympani - terminal branch of the nervus intermedius carrying both secretomotor fibres to the submandibular gland and sublingual gland and taste to the anterior two thirds of the tongue.
- nerve from the auricular branch of the vagus nerve (CN X) - pain fibers to the posterior part of the external acoustic meatus hitchhike from the jugular foramen.
Typically enhancement is seen:
- anterior genu (geniculate ganglion)
- posterior genu (between tympanic and mastoid segments)
- some enhancement can also be seen in the labarynthine, tympanic and mastoid segments.
- proximal greater superfical petrosal nerve
No enhancement should be seen in:
- cisternal segment (that in the cerebellopontine angle)
- meatal segment (that in the internal acoustic meatus)
- extracranial segment (beyond the stylomastoid foramen)
Spine
- If shown a lateral C-spine film, think of three things
- trauma (fx)
- abscess
- mass
- Terminal Ventricle
- cavity at the level of the conus medullaris
- normal variant
- seen almost exclusively in children <5 yrs old
- if persistent, may be associated with tethered cord
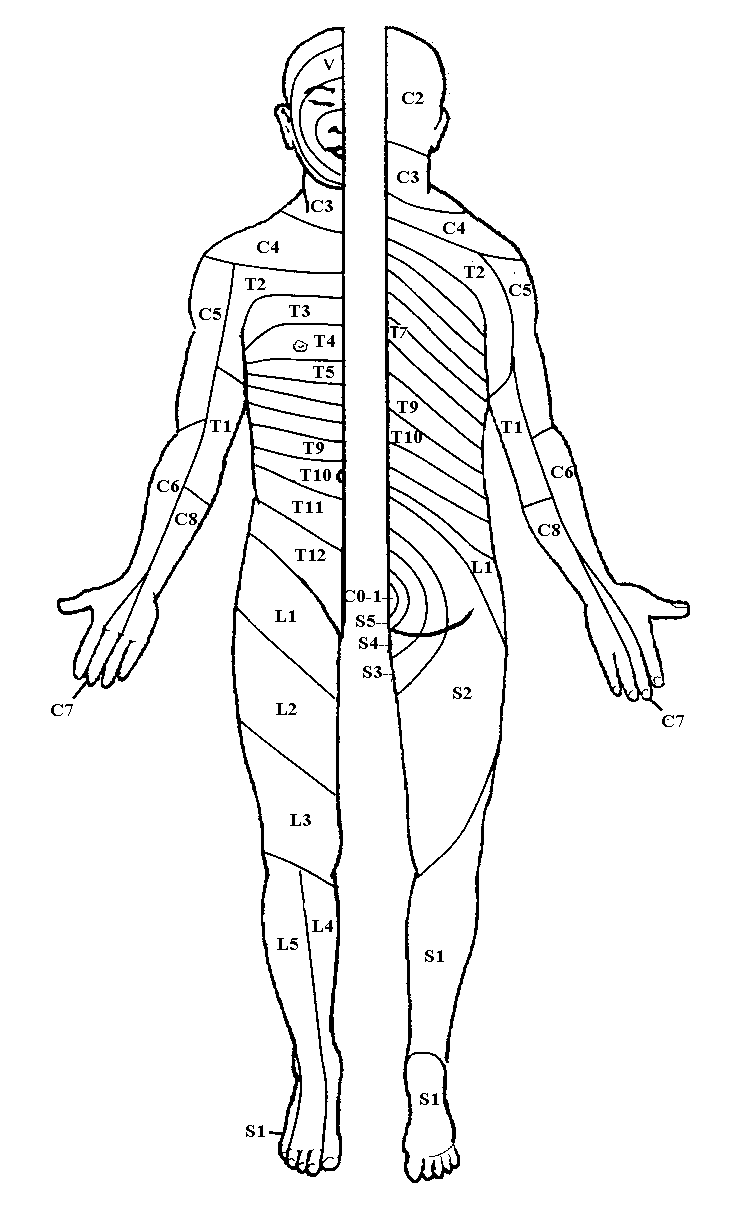
Dermatomes
DDx
Intradural Intramedullary
- astrocytoma
- infiltrating
- most common in C-spine
- ependymoma
- central, well-defined, cystic changes, hemorrhage, patchy enhancement
- most common at conus
- hemangioblastoma
- feeding vessel (flow voids)
- cystic component
- most common in C-spine
Intradural Extramedullary
- schwannoma
- neurofibroma
- meningioma
- drop mets
- arachnoid cyst - usually thoracic spine, posterior
- epidermoid cyst
Extradural
- disk
- meningioma
- schwannoma
- neurofibroma
- mets/myeloma/lymphoma
- epidural abscess
- epidural hematoma
- synovial cyst
- leptomeningeal enhancement
- sarcoid
Transverse Myelitis
- Parainfectious (occurring at the time of and in association with an acute infection or an episode of infection).
- Viral: herpes simplex, herpes zoster, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses (poliomyelitis, Coxsackie virus, echovirus), human T-cell, leukemia virus, human immunodeficiency virus, influenza, rabies
- Bacterial: Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Lyme borreliosis, syphilis, tuberculosis
- Postvaccinal (rabies, cowpox)
- Systemic autoimmune disease
- Systemic lupus erythematosis
- Sjogren's syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Paraneoplastic syndrome
- Vascular
- Thrombosis of spinal arteries
- Vasculitis secondary to heroin abuse
- Spinal arterio-venous malformation
Enhancing Nerve Roots (cauda)
- drop mets
- sarcoid
- leukemia, lymphoma
- CMV
- Guillan-Barre
- CIDP (also enlarged)
- meningitis
Cord Infarct
- Snake eyes appearance on axial imaging
- Anterior spinal artery infarct
- Increased T2 in central gray matter
DDx Heterogeneous Marrow Signal
- normal variant
- anemia
- chronic disease
- neoplastic processes such as lymphoma, metastatic disease, or myelodysplastic syndromes.
Loss of Fatty Marrow
- Lymphoma
- Extramedullary Hematopoesis
- Myelofibrosis
- (XRT will increase fatty marrow)
Dorsal Column Increased Signal
- B12 deficiency
- Syphillis
Epidural Lipomatosis
- Cushing's Dz
- Steroids
- Congenitalß
Posterior Element Lesion (GO APE)
- Giant Cell
- Osteoblastoma/Osteoid Osteoma
- ABC
- Plasmacytoma
- EG
Vertebral Body Lesion (CALL HOME)
- Chordoma
- ABC
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Hemangioma
- Met/Myeloma
- EG
Posterior Scalloping
- Increased Intraspinal Pressure
- Tumor
- Syrinx
- Communicating HCP
- Dural Ectasia
- NF-1
- Marfan
- Ehlers-Danlos
- Congenital
- Achondroplasia
- Mucopolysaccharidoses → Hunter/Hurler/Morquio's (look for beaking
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta Tarda
- Bone Resorption
- Acromegaly
Hemivertebrae
- VACTERL
- NF-1
- Chiari II
- Anterior Meningocele
Benign vs Malignant Compression Fractures
- Malignancy tends to involve the pedicles, whereas benign does not
- Look for other levels of involvement - if you see noncompressed vertebral bodies at other levels which also have abnormal signal, then you can assume malignant
- Cortical destruction is a feature of malignancy
- Malignant frxs tend to show abnormal T1 signal involving >80% of the v.b., benign has less
Orbits
Orbital DDx
Intraconal
- cavernous hemangioma (capillary in children)
- schwannoma
- lymphangioma
- varix
- optic n tumor (meningioma, glioma)
- pseudotumor - pain, opthalmoplegia, proptosis, unilateral, enlarged lacrymal gland
- Tolosa-Hunt involves orbital apex and cavernous sinus
- thyroid opthalmopathy - spares tendon insertions, often bilateral, does not enhance
- lymphoma
Extraconal
- lacrymal gland
- lymphoma, pseudotumor
- sinus disease
- mucocele, invasive infections, neoplasm
- orbital bone disease
- fibrous dysplasia, osteomyelitis, subperiosteal abscess, tumors, trauma
- nasal disease
- infection, neoplasm
- dermoid
- rhabdomyosarcoma
- common in children
- mets
Extraocular Muscle
- mets
- inflammation
- thyroid eye disease
- bilateral
- sparing of muscle tendons
- pseudotumor
- lymphoma
Lacrymal Gland
- lymphoma
- sarcoid
- inflammatory
- Sjogren's
- Miukulicz's
- epithelial tumors
- pleomorphic adenoma
- adenoid cystic
- mucoepidermoid
- mets
Optic Nerve Pathology
- use term 'optic nerve sheath complex'
- Optic Neuritis → hyperintense, enlarged
- Glioma → enlarged nerve, do not enhance
- Meningioma → crescentic
- Sarcoid → enhances
- Lymphoma/leukemia
- Pseudotumor
- Graves
Globe
- Retinoblastoma
- intraocular mass
- high density (Ca2+, hemorrhage)
- 30% bilateral
- Melanoma
- thickening of choroid, usually posterior
- usually unilateral
- high T1, low T2 with enhancement
- Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous
- unilateral small globe
- no calcification
- Coats' Disease
- unilateral dense vitreous w/ focal mass or Ca2+
- Drusen
- focal Ca2+ in optic nerve head
- usually bilateral and asymptomatic
- may be mistaken for papilledema
Temporal Bone
DDx for mass in mesotympanum
- aberrant ICA
- glomus tumor (tympanicum)
- cholesteatoma
Nasal Cavity/Sinuses
Maxillary sinus lesion extending to base of tooth? → Think dentigerous cyst
Esthesioneuroblastoma has a bimodal age distribution → children (11-20) and older adults (51-60)
Mucocele Characteristics
- Expansion of sinus
- Complete filling of sinus
- Order of prevalence = FEMS (frontal>ethmoid>maxillary>sphenoid)
Inverting Papilloma
- typically arises from the lateral nasal wall and extends into the ipsilateral ethmoid or maxillary sinus
- worry about coexisting SCC (common)
Antrochoanal Polyp
- benign polyp arising in antrum and extending into the nasal cavity
- no sinus expansion
Temporal Bone Fxs
| Transverse | Longitudinal |
|---|---|
| Sensorineural Hearing Loss | Conductive Hearing Loss |
| rhinorrhea | otorrhea |
| 50% facial nerve dysfunction | 10-20% facial nerve dysfunction |
| persistent vertigo | incudostapedial joint dislocation |
Head & Neck
Sjogren's can look like fatty replaced salivary glands
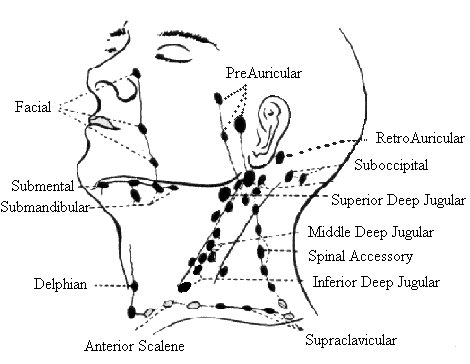
Lymph Node Levels
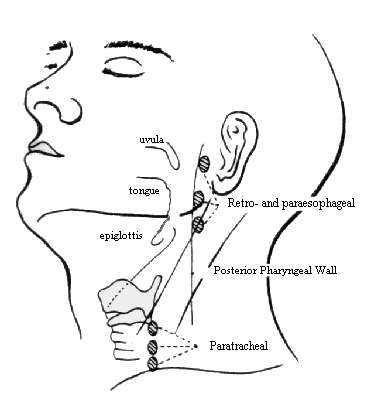
Lymph Node Chains
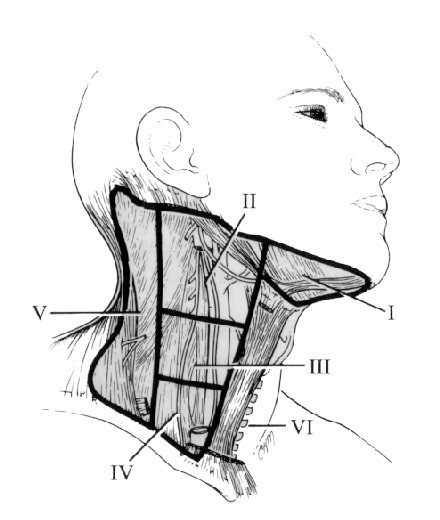
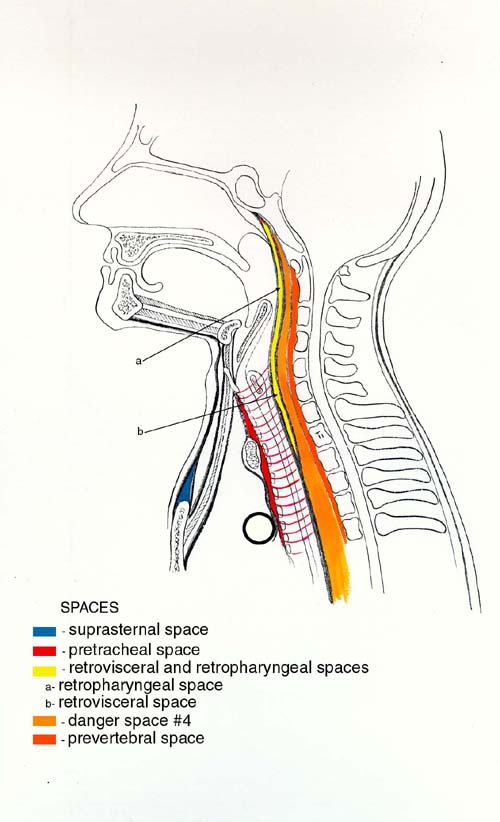
Spaces of the Neck
Neoplasms
Most Common Intraaxial Tumors
| Location | Adult | Child |
|---|---|---|
| Supratentorial | Astrocytoma * Pilocytic * Anaplastic * GBM Oligodendroglioma Gliomatosis Cerebri Metastasis | PXA PNET Ganglioglioma/Gangliocytoma Desmoplastic Infantile Ganglioglioma (DIG) DNET |
| Infratentorial | Astrocytoma Hemangioblastoma Metastasis Subependymoma Ganglioglioma | Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma PNET/Medulloblastoma Ependymoma Brainstem Astrocytoma |
| Intraventricular | Meningioma Metastasis Central Neurocytoma Subependymoma Astrocytoma Oligodendroglioma CP papilloma (4th vent) | CP papilloma/carcinoma (atria) Ependymoma Astrocytoma PNET Teratoma |
| Spinal |
* Probably should add lymphoma to all of these, especially in HIV pts
Intraventricular Mass
- Child
- PNET/Medulloblastoma
- usually 4th ventricle, but can be in lateral vents
- Choroid Plexus Papilloma/Carcinoma
- lateral ventricles
- always have hydrocephalus
- Ependymoma
- Teratoma
- Astrocytoma
- Adult
- Meningioma
- Central Neurocytoma
- Gliomas → Subependymoma, Astrocytoma
Extra-axial Mass
- Meningioma
- Hemangiopericytoma
- Schwannoma
- Metastases
- Lymphoma
- Dermoid
- Epidermoid
- Arachnoid cyst
- Bone neoplasm or infection
- Leukemia
- Sarcoidosis
Lesions which cross the corpus callosum
- GBM
- Lymphoma
- Tumefactive MS (horseshoe enhancement)
One-Liners
Subependymal Spread Pattern → think of pineal germinoma
Paraneoplastic Syndromes
Limbic Encephalitis
- high T2 signal in medial temporal lobes
- may have associated atrophy
- may enhance
- associated with small cell lung CA
Infectious
HSV Encephalitis
- temporal lobe involvement
- may or may not enhance
- restricted diffusion
Creuzfeld-Jakob Disease
- T2 hyperintense areas in cortex and basal ganglia which restrict
- no enhancement
Trauma
- Skull fractures that are accompanied by dural tears can result in the formation of a leptomeningeal cyst = “Growing Fracture”
Diffuse Axonal Injury
- responsible for coma and poor outcome in the majority of patients with significant closed head injury
- specific anatomic structures involved
- body and splenuim (most common location) of the corpus callosum
- septum pellucidum
- dorso-lateral quadrant of the rostral part of the brainstem
- adjacent to the superior cerebellar peduncle
- diffuse damage to other axons including the int. capsule may also be present
- punctate subcortical hemorrhage and hemorrhage in WM adjacent to the 3rd vent also occur
Random
Mets are very unlikely in the brainstem
Superficial Siderosis
- low signal intensity in periphery of midbrain, particularly posterior
Rhomboencephalosynapsis
- rare malformation with vermian aplasia or hypoplasia with fusion of the cerbellar hemispheres
- no 4th ventricle midline defect
- associated with fusion of the thalami and/or inferior colliculi
- associated with septo-optic dysplasia
Lhermitte-Duclos
- cerebellar hamartoma
- courdoroy appearance w/ calcification
- related to Cowden syndrome
Wernicke's encephalopathy
- increased signal within the periaqueductal region of the midbrain, medial thalamic regions along the lateral walls of the third ventricle, and mammilary bodies
- triad of opthalmoplegia, ataxia, and altered mental status
- related to alcohol abuse
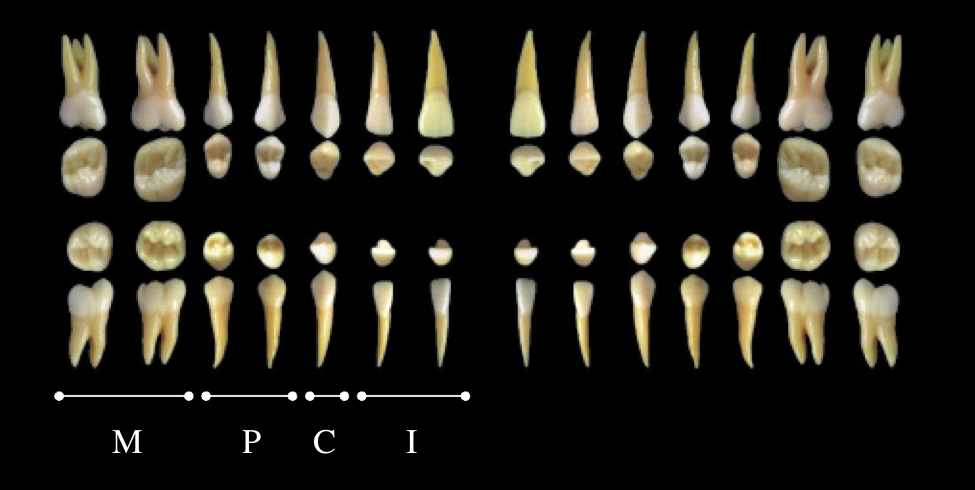
Dental
Differentials
PRES vs basilar territory infarct
- PRES
- Mostly FLAIR abnormality
- Vasogenic edema
- Thalamus usually spared
- Basilar territory infarct
- Restricted diffusion
- Matched DWI/FLAIR abnormality
- Vascular territory
Dark spots on GRE
- Amyloid angiopathy
- Hypertensive microbleeds
- Cavernomas (familial)
- DAI
- Calcifications
- Hemorrhagic mets
Ring-enhancing lesion
- Metastasis
- Multiple lesions with rim enhancement
- No restricted diffusion
- Glioblastoma
- Shaggy enhancement
- Lymphoma
- Increased diffusion due to cellularity
- NOT lightbulb bright on DWI
- Abscess
- Restricted diffusion
- Lightbulb bright on DWI
Parenchymal Hemorrhage
- Hypertensive (75%)
- AVM
- Dural AVF
- DVA
- Cavernous malformation
- Capillary telangiectasia
- Aneurysm
- Amyloid angiopathy
- Vasculitis
- Infarct
- Dural venous thrombosis
Basal Ganglia Calcification
- Senescent
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Pseudo and Pseudo-pseudohypoparathyroidism
- Hyperparathyroidism
- TORCH
- AIDS
- TB
- Lead
- CO
- XRT/Chemo
- Mitochondrial diseases
- Fahr syndrome
Diffuse Subcortical Calcifications
- Prior Infection
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Lead Exposure
- Leukemia
- Prior XRT
Basal Ganglia Hyperintense T1 (HTN)
- TPN (Manganese)
- Hepatic failure
- NF-1
- Dystrophic calcifications
Basal Ganglia Hyperintense T2 (TINT)
- Tumor
- Lymphoma
- Ischemia
- Hypoxic encephalopathy/Near drowning
- Venous infarction
- Neurodegenerative
- Huntington's
- Wilson's disease - bright T2 peripherally, dark centrally
- Hallevorden-Spatz - bright T2 centrally, dark peripherally
- Leigh - uniformly bright T2, involves pons, does not involve caudate
- Kearns-Sayre
- Toxin
- CO, CN poisoning
- hypoglycemia
- methanol
Basal Ganglia Hypointense T2
- Old age
- Chronic degenerative disease
- Parkinson's
- MS
- Childhood hypoxia
Corpus Callosum Lesion
- GBM - will see edema
- Lyphoma - homogeneously enhancing
- XRT
- MS
- Marchiafava-Bignami
Basimeningeal Enhancement
- Basically STL → Sarcoid, TB, Lymphoma
- Infection
- TB
- Fungal
- Pyogenic
- Cysticercosis
- Tumor
- Leukemia/Lymphoma
- Carcinomatosis
- Inflammatory
- Sarcoid
- Rheumatoid
- Whipple's Disease
Low Lying Cerebellar Tonsils
- Chiari I/II
- Intracranial Hypotension
- Mass Effect
Involvement of Cerebellar Peduncles
- MS
- Sinus Thrombosis
- Olivopontocerebellar Atrophy
- It's all in the name → ataxia/dementia syndrome w/ cerebellar and brainstem atrophy
Leptomeningeal Enhancement
- Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
- Meningitis
- Sarcoid, TB, Lymphoma
Layering Restricting Material in Vents
- Blood
- Pus (Ventriculitis)
Brainstem Hemorrhage
- Hemorrhagic Infarct
- Trauma (usually anterior → Duret hemorrhage)
- AVM
- DAI
Obstruction at Aqueduct of Sylvius
- Aqueductal Stenosis
- “Pencil” Glioma → surrounding the aqueduct
Suprasellar Cystic Mass
- Rathke Cleft Cyst
- Simple, uniloculated
- craniopharyngioma (calcification)
- JPA
Jugular Foramen Mass
- Paraganglioma - aggressive appearance
- Schwannoma
- Meningioma
Anterior Neck Cyst
- Thyroglossal Duct Cyst
- Delphian Lymph Node
- Lymphangioma
Parotid Cysts
- Lymphoepithelial
- Branchial Cleft
- Lymphangioma
- Abscess
- Cystic Tumors
Bilateral Parotid Cysts
- Warthin's Tumor
- Sjogren's
- Lymphoepithelial Cysts
- Lymph Nodes → Lymphoma, Skin Cancers
- Sarcoid
Horner's Syndrome
- ICA Dissection
- Tumor along course of ICA
- Pancoast Tumor
Diffuse Skull Thickening
- Anemias → ß-thal
- Osteopetrosis
- Paget's
Focal Non-destructive Skull Widening
- Meningioma
- Fibrous Dysplasia
Lytic, Non-aggressive Skull Lesion
- Epidermoid
- Fibrous Dysplasia
Pediatric Skull Lesion
- EG
- Metastatic Neuroblastoma
Basilar Invagination
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Achondroplasia
- Down Syndrome
Etat Crible
- Small foci of increased signal in the basal ganglia
- Causes:
- lacunar infarctions
- gliosis
- dilated perivascular spaces
- demyelination
- nonspecific protein depositions
- cysts
- ventricular diverticuli