Table of Contents
Vascular
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Aneurysm is a dilatation of more than 3 cm OR
- an increase in diameter of 50% greater than original artery
- The majority of the abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) are infrarenal
- The correct measurement technique is outer wall to outer wall
- Common iliac aneurysm
- > 1.7 cm (male)
- > 1.5 cm (female)
DDx for ↑ resistance waveforms
- Peripheral artery; distal aorta
- Proximal to stenosis/ occlusion
- Renal transplant rejection
DDx for ↓ resistance waveforms
- Organs: brain; liver; kidney; etc.
- Placenta
- AVM / AVF
Carotids
- Surgical candidates
- Symptomatic patients with stenosis > 70% (NASCET = North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial)
- Asymptomatic patients with stenosis > 60% (ACAS = American Carotid Atherosclerosis Study)
- ICA occlusion: absence of blood flow; externalization of CCA
| Features | ICA | ECA |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Posterolateral | Anteromedial |
| Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Branches | None | Several |
| Waveform | ↓ resistance | ↑ resistance |
| Temporal tap | No | Yes |
| % Stenosis | PSV | EDV | PSV Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 70-100 | ||
| 50-69% | >130 | >1.8 | |
| 70-95% | >250 | >100 | >4 |
| >95% | Velocity falls |
Renal Artery Stenosis
| % Stenosis | PSV | RAR | SAT | Waveform |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | <180 | <0.1 | Low resistance | |
| <60% | >180 | <3.5 | <0.1 | Low resistance |
| >60% | >180 | >3.5 | >0.1 | Poststenotic turbulence Doppler bruit or plaque |
* Cannot use the RAR if:
- If AAA detected
- If aortic PSV > 90cm/s or < 40cm/s
- If one of these conditions is present, look at the Renal Artery PSV only
Renal RI's
RI = (peak systolic velocity - end diastolic velocity ) / peak systolic velocity
- the normal value is ≈ 0.60
- > 0.70 is abnormal
Usefulness of RI is limited
Mesenteric
- SMA stenosis
- PT MUST BE FASTING
- PSV > 275 cm/s indicates a > 70% diameter reduction
- Post-prandially
- The celiac artery remains a low resistance vessel
- The SMA becomes low resistance, because now it needs more blood for digestion
- If the SMA does not change dramatically after eating, there is a stenosis/occlusion
- Low resistance abdominal arteries
- renal
- celiac
- hepatic
- High resistance abdominal arteries
- Aorta
- fasting SMA
- fasting IMA
Lower Extremity Arterial
| % Stenosis | PSV | PSV Ratio | Waveform shape | Waveform window |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 70-120 | Normal | Triphasic | Clear window |
| 1-19% | Normal | Normal | Triphasic | Spectral broadening |
| 20-49% | 120-180 | <2:1 ratio | Triphasic | Spectral broadening |
| 50-99% | >180 | >2:1 ratio | Loss of flow reversal | Spectral broadening |
Ankle Brachial Index
- ABI < 0.95 at rest or following exercise is considered abnormal
- ABI between 0.8 and 0.95 is mildly decreased
- ABI between 0.5 and 0.8 is consistent with moderate disease/intermittent claudication
- ABI < 0.5 indicates severe disease
- Use the higher of the two ankle pressures for the ABI
Toe Brachial Index
- 0.80 -0.90 normal
- 0.20 -0.35 intermittent claudication
- <0.20 rest pain/ischemia
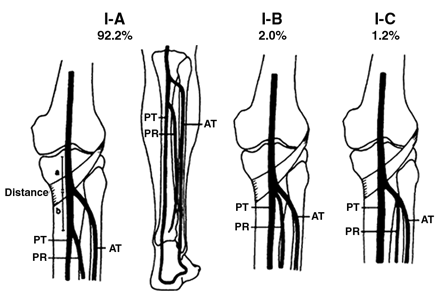
Trifurcation Anatomy
TIPS
| Diagnosis | Stent | MPV | RPV, LPV | RHV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 80-190 | >30 | one or both retrograde | 80-190 |
| Abnormal | >190 or <80 >50 interval Δ color bruit or stenosis | <30 | antegrade | >190 |
Thyroid
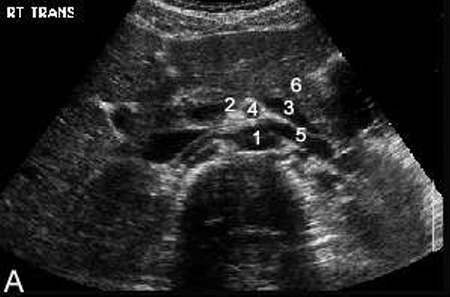
Anatomy
Recommendations for Thyroid Nodules 1 cm or Larger in Maximum Diameter
| US Feature | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Solitary nodule | |
| Microcalcifications | Strongly consider US-guided FNA if ≥ 1 cm |
| Solid (or almost entirely solid) or coarse calcifications | Strongly consider US-guided FNA if ≥ 1.5 cm |
| Mixed solid and cystic or almost entirely cystic with solid mural component | Consider US-guided FNA if ≥ 2 cm |
| None of the above but substantial growth since prior US examination | Consider US-guided FNA |
| Almost entirely cystic and none of the above and no substantial growth (or no prior US) | US-guided FNA probably unnecessary |
| Multiple nodules | Consider US-guided FNA of one or more nodules, with selection prioritized on basis of criteria (in order listed) for solitary nodule |
- Note: FNA is likely unnecessary in diffusively enlarged gland with multiple nodules of similar US appearance without intervening parenchyma. Presence of abnormal lymph nodes overrides US features of thyroid nodule(s) and should prompt US-guided FNA or biopsy of lymph node and/or ipsilateral nodule.
Liver
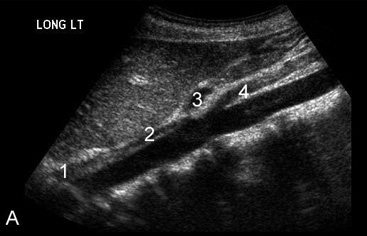
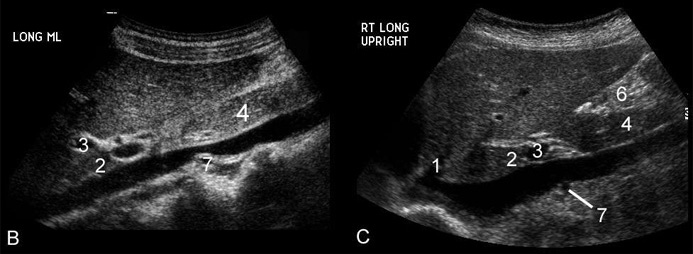
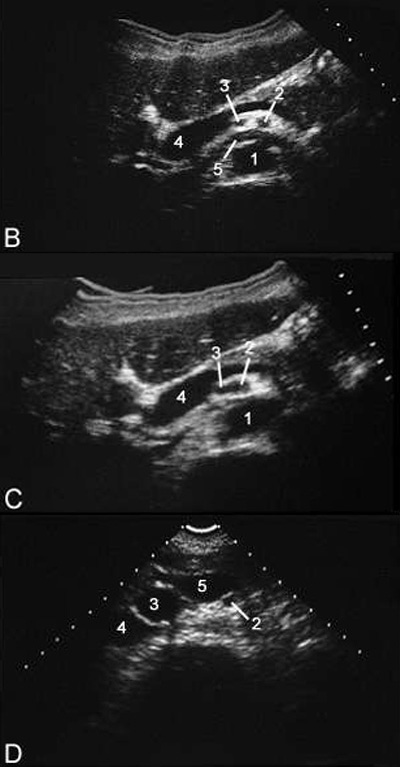
Anatomy
- Ligamentum teres → obliterated umbilical vein
- Ligamentum venosum → remnant of ductus venosus
- Common duct is straighter and more variable in diameter than hepatic artery
- Right hepatic artery is normally between portal vein and bile duct
- Upper limit of normal for intrahepatic bile ducts = 2 mm
Hyperechoic Liver Mass
- Hemangioma
- HCC
- Focal Fat
Thickened Gallbladder Wall
Normal GB wall < 3mm
- heart failure
- hypoproteinemia
- edema-forming states
- hepatitis
- cirrhosis
- portal hypertension
- lymphatic obstruction
- GB cancer
- adenomyomatosis
- cholecystitis
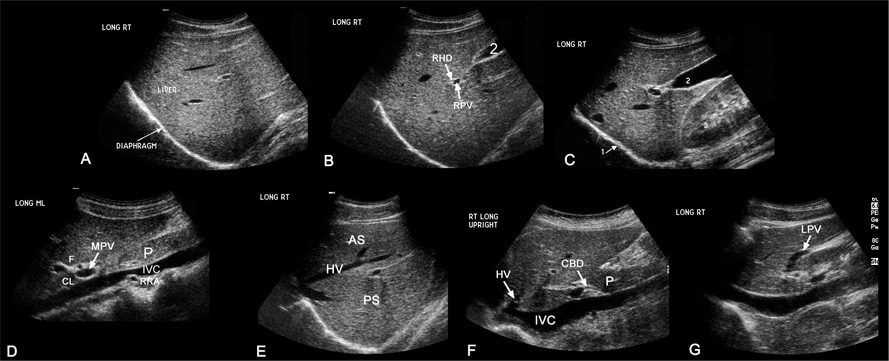
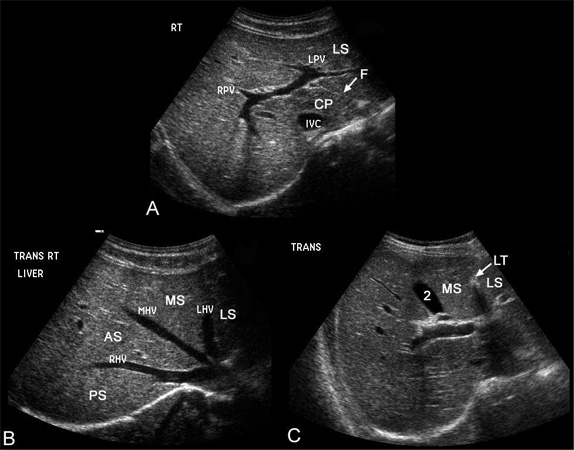
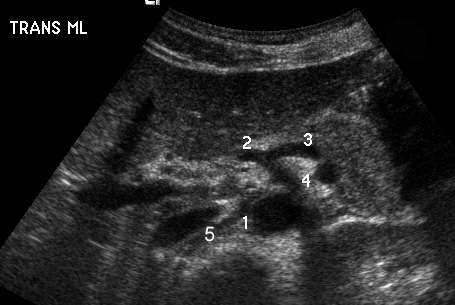
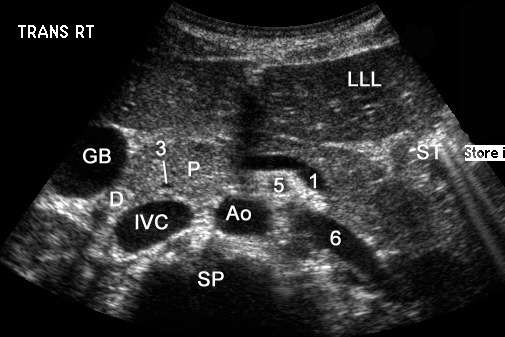
Upper Abdominal Vascular Anatomy
Spleen
- Upper limit of normal → 13 cm
Hypoechoic Masses
- lymphoma
- mets
- sarcoid
- infarcts
- infection
Pancreas
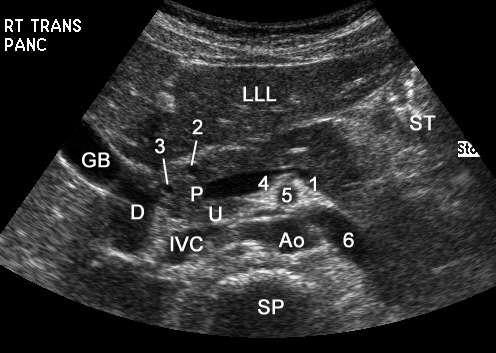
Anatomy
Renal
Bosniak Classification of Renal Cystic Disease
- Category I — Category I lesions are simple benign cysts showing homogeneity, water content, and a sharp interface with adjacent renal parenchyma, with no wall thickening, calcification, or enhancement.
- Category II — This category consists of cystic lesions with one or two thin (≤ 1 mm thick) septations or thin, fine calcification in their walls or septa (wall thickening > 1 mm advances the lesion into surgical category III) and hyperdense benign cysts with all the features of category I cysts except for homogeneously high attenuation. A benign category II lesion must be 3 cm or less in diameter, have one quarter of its wall extending outside the kidney so the wall can be assessed, and be nonenhancing after contrast material is administered.
- Category IIF — This category consists of minimally complicated cysts that need follow-up. This is a group not well defined by Bosniak but consists of lesions that do not neatly fall into category II. These lesions have some suspicious features that deserve follow-up up to detect any change in character.
- Category III — Category III consists of true indeterminate cystic masses that need surgical evaluation, although many prove to be benign. They may show uniform wall thickening, nodularity, thick or irregular peripheral calcification, or a multilocular nature with multiple enhancing septa. Hyperdense lesions that do not fulfill category II criteria are included in this group.
- Category IV — These are lesions with a nonuniform or enhancing thick wall, enhancing or large nodules in the wall, or clearly solid components in the cystic lesion. Enhancement was considered present when lesion components increased by at least 10 H.
Hydronephrosis
- Grade 1 - minimal separation of renal sinus
- Grade 2 - distention of collecting system
- Grade 3 - marked distention with cortical thinning
Lesions That Simulate Cysts
- Calyceal Diverticulum
- Aneurysm/Pseudoaneurysm
- Lymphoma
- Upper Pole Duplication
Prostate
Anatomy
- peripheral zone (hyperechoic; develops into carcinoma)
- transitional zone (periurethral; hypoechoic; ↑ BPH)
Prostate carcinoma
- hypoechoic lesion in peripheral gland (70%); nodular or diffusely infiltrative
- DDX = prostatitis; fibrosis; infarct; BPH; correlate with PSA/ DRE and BX
- normal PSA < 4 ng/mL
BPH
- enlargement of transitional zone; inhomogeneity; Ca2+
Prostatic cysts
- Midline: utricle cyst; Muellerian duct cysts; ejaculatory duct cysts
- Eccentric/ paramedian: seminal vesicle cysts; retention cysts; cystic BPH
Scrotal
Extra-testicular masses
- Spermatocele: most common extratesticular mass; ↑ head of epididymis
- Epididymal cysts: head or tail of epididymis
- Adenomatoid tumor: #1 extra-testicular neoplasm; most common tumor of epididymis (> sarcoma; leiomyosarcoma; metastases)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma: ↑ children
- Hydroceles: fluid within tunica vaginalis; may develop cholesterol crystals → internal echoes (DDX = pyocele; hematocele)
- Varicocele: dilated peritesticular veins (= pampiniform plexus); left (85%) > right (venous drainage); ↑ infertility
- Tunica albuginea cysts
Intra-testicular masses
- Testicular cysts: rare; ↑ elderly; ↑ near mediastinum (tunica albuginea)
- Tubular ectasia of rete testis: usually bilateral; ↑ spermatoceles and intratesticular cysts
- Seminoma: most common germ cell tumor; radiosensitive; ↑ young males; homogeneously hypoechoic
- Teratomas: complex cystic masses; benign (children) or malignant (adult)
- Embryonal cell carcinoma and choriocarcinoma: malignant; heterogeneous
- Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors: rare; non-germ cell (= stromal) tumors; solid masses; < 6 years
- Epidermoid cysts: benign; only ectodermal derivatives
- Metastases: lymphoma; leukemia; prostate > lung, colon
- Other lesions: focal orchitis; infarcts; atrophy; hematomas; abscesses
Testicular microlithiasis
- > 5 Ca2+ per image; ↑ germ cell tumors
Testicular torsion
- ↑ risk with bell-clapper deformity (abnormal tunica vaginalis suspended by spermatic cord); venous obstruction→ arterial obstruction → ischemia; DX w/in 6 hrs;↓ BF
Epididymo-orchitis
- inflammatory hyperemia with testicular enlargement and ↓ echogenicity
DDx Focal Hypoechoic Mass
- tumor
- seminomas → homogeneously hypoechoic
- non-seminomas → heterogeneous
- infarct
- focal atrophy
- focal orchitis
- hematoma
- abscess
- sarcoid
- contusion