nukes
Table of Contents
Infection/Inflammation
In 111 WBC
- active inflam/infx
- spleen>liver>bone
- 1 hr IBD
- 4 hr abdomen
- 24 hr whole body
In 111 WBC w/ SC
- since In-WBC can be hot with marrow activation, get SC scan
- if In-WBC is hot and SC cold, then likely infected
- if both hot, then just bone marrow activation
Ga 67
- iron analogue
- goes where iron goes - salivary and lacrymal glands, liver, bowel
- can see cardiac activity for the first few hours
- if cardiac activity persists, ddx myocarditis, pericarditis, lymphoma, amyloid, sarcoid
- used for inflammation, diskitis
- should not see renal act after 24h
- pulmonary gallium score - used to evaluate sarcoid response to therapy
Tc MDP
- 140 kev
- flow 60s
- pool 5m
- delay 2-3h
- kidneys, liver, breast, lung, extremities
- ddx increased liver uptake - mets from mucinous adenoCA, amyloid, acute hepatic necrosis, impurities
Thyroid/Parathyroid
General
- Palpate gland and ask for RAIU for every scan
- RAIU can be determined using either I-131 (7 µCi) or I-123 (200-300 µCi)
- Nl 4hr RAIU = 5-15%
- Nl 24hr RAIU = 10-30%
Therapy
Contraindications to I-131 therapy
- Pregnancy: Radioiodine freely crosses the placenta. Additionally, activity in the maternal bladder causes significant fetal irradiation. The fetal thyroid extracts/concentrates iodine after the 12th week and the radiation will destroy the thyroid gland and result in severe hypothyroidism.
- Breast feeding: Both iodine and pertechnetate are excreted in breast milk
- Severe thyrotoxicity: Patients should be pretreated (with beta-blockers) to avoid thyroid storm which can occur from sudden release of hormones following radiation destruction of the thyroid follicles
Drug interactions
| Medication | Withdrawl Period |
|---|---|
| Antithyroid medication (propylthiouracil, methimazole, carbimazole) and multivitamins | 3 days for antithyroid medication 7 days for multivitamins |
| Thyroid hormone | 2 weeks for cytomel 4 to 6 weeks for synthyroid |
| Kelp, Lugol's solution, SSKI solution | 2 to 3 weeks |
| IV contrast | Over 1 month |
| Amiodarone | 3 to 6 months |
Alternatives
- PTU, surgery, do nothing
Dose calculations
- complicated - (rads * wt of gland) / (900 * RAIU)
- simplified - (0.12mCi * wt of gland (in grams)) / % uptake
- easiest - empirically treat 12mCi for Graves and 29.9mCi for multinodular goiter
Thyroid Patterns
- graves - increased RAIU
- acute - no uptake or patchy faint uptake
- subacute - decreased uptake
- hashimoto's - can be either decreased or increased (rare) uptake
Congenital
- Thyroid dysgenesis (anatomic abnormalities) - aplasia, hypoplasia, or ectopy of the thyroid gland, often with hypoplasia
- insufficient tissue to match the demands
- abnormal anatomy is seen on thyroid scanning
- Dyshormonogenesis (organification defects) - serious error in thyroid hormone synthesis
- thyroid trapping of pertechnetate or iodine will be increased
- Hypopituitarism (secondary hypothyroidism) - pituitary aplasia or midline brain developmental defects
- may also be hypothalamic dysfunction (tertiary hypothyroidism)
- anatomically normal thyroid will show reduced uptake
- Pendred syndrome
- sensorineural hearing loss
- goiter, usually not present until puberty at which time the thyroid becomes diffusely enlarged
- affected individuals generally remain euthyroid despite the goiter
- thyroid defect is associated with abnormal iodide processing, that often can be diagnosed using the perchlorate discharge test
- potassium perchlorate - competitive inhibitor of iodide transport into the thyroid
I 123
- dose → 200-400 µCi orally
- 4h image, 24 RAIU
- thyroid, gastric, renal/bladder, salivary glands, NP, liver
- better resolution than 131I
- not used much b/c of cost
I 131
- 369 keV
- uptake in thyroid, kidneys, stomach, colon, and salivary glands
- liver activity if functioning thyroid tissue present
- Doses:
- 30-50 µCi thyroid scan
- 2-5 mCi cancer f/u
- 20-30 mCi therapy for toxic multinodular goiter
- 100-200 mCi for thyroid carcinoma
- imaging done @ 48-72 hr to reduce background
- liver uptake means funct thyroid tissue or tumor present
- contraindicated during pregnancy (crosses placenta)
Short-term complications
- sialadenitis
- gastritis
- azoospermia
- thyroid storm
Long-term complications
- pulmonary fibrosis
- bone marrow depression
- lymphoma/leukemia
- hypothyroidism
Pertechnetate
- trapped by the thyroid gland in the same manner as iodine (an active transport mechanism)
- after trapping pertechnetate slowly “washes” from the gland → it does NOT undergo organification
- typical dose is 3 mCi IV
- do NOT need to stop PTU
- PTU blocks oxidation and organification of iodide following its uptake by the thyroid gland, but will not interfere with trapping of pertechnetate
Tc sestamibi
- mitochondrial uptake
- early = 10-20 min, thyroid & parathyroid visible
- late = 2-3 hours, thyroid washes out
Causes of increased activity on delayed images:
- parathyroid adenoma - focal uptake w/ history of hypercalcemia
- thyroid cancer / thyroid adenoma - less likely possibilities
- parathyroid hyperplasia - multiple foci of increased uptake
Liver
IDA
- cardiac bp clears in < 5m
- uniform liver activity at 15 min
- gallbladder seen < 30m
- sm bowel < 1h
- no GB @ 4h dx acute chole
- 2mg morphine (do not give until you see bowel) or 24h delay
- 0.04 mg/kg per Evan protocol
- ideal prep is npo for 4-12 hrs
- if npo for greater than 24 hrs, the GB will be full
- don't scan preemies right away (false positives)
Gallbladder Ejection Fraction
- Normal: ≥50%
- Borderline: 35-49%
- Decreased: <35%
Delayed Biliary to Bowel Transit
- Nonspecific finding which can be secondary to:
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Partial common bile duct obstruction
- Can be a normal variant in up to 20% of patients
Tc SC
- Ratio of Liver:Spleen:Bone Marrow = 80:15:5
- Colloid shift = portal HTN
- FNH is basically the only liver mass to take up SC (Kupffer cells)
Gastric Emptying
- Normal solid phase emptying: 50% by 90-120 minutes.
- Normal liquid phase emptying: 50% by 60 minutes.
Oncology
PET
- Prep
- NPO after midnight
- no physical activity
- cold, dark room with no stimulation
- feed the heart, starve cancer - means give glucose + insulin prior to cardiac PET; fasting for cancer studies
- flare effect - SUVs will temporarily (first several weeks) rise after Tamoxifen therapy for breast CA in responders. In nonresponders, SUVs will remain stable.
I 131 MIBG
- pheo, neuroblastoma, many other tumors
- drugs block MIBG → cocaine, TCA, thorazine, CCB, B-blockers
- must protect thyroid w/ supersat iodine (Lugol's)
In 111 octreoscan (pentreotide)
- spleen, kidneys, bladder, liver
- neuroendocrine tumor, glioma, pit ad, breast, granulomatous dz, MTC
In 111 Prostascint
- look for L supraclavicular node = Virchow node
Neuro
Brain perfusion study or FDG-PET
- Indications
- Dementia
- Alzheimers - decreased parietotemporal activity
- Pick's - decreased frontal activity
- Multi-infarct dementia - multiple defects, vascular territories, superficial or deep
- Dementia with Lewy bodies - diffuse glucose hypometabolism, particularly in the occipital region
- Seizure focus
- usually done interictal - decreased activity in area of seizure focus
- Residual tumor vs. radiation
- residual tumor will have uptake, radiation will not
- Toxo vs. lymphoma
- lymphoma will have uptake
- Others
- Contusion
- Malignancy
- uptake < gray matter → low-grade tumor (WHO grade 1-2)
- uptake gray matter → high-grade tumor (WHO grade 3-4)
Brain flow
- can be done w/ any agent
- good bolus, must see B carotids
- hot nose - secondary sign = nonspecific
- trident sign - visualization of MCA(lateral) ACA(middle)
- can't suggest brain death if patient is hypothermic
Cisternogram
- LP injection
- 30m intrathecal
- 4h basal cisterns
- 24h convexities
- 48h clearance
- ind- comm HCP, CSF leak
Pulmonary
General
- ALWAYS ask for CXR
PIOPED
High Probability
- 80-100% likelihood for PE
- Greater than or equal to 2 large mismatched segmental perfusion defects or the arithmetic equivalent in moderate or large and moderate defects. A high probability lung scan confirms a very high likelihood for pulmonary embolism and justifies treatment with anticoagulation (unless contraindicated)
- It has been suggested that 2.5 mismatched large segmental defects (or the arithmetic equivalent) is a better threshold for calling a scan high probability, as it associated with a 100% probability of PE in the PIOPED population
Intermediate Probability
- 20-80% likelihood for PE
- One moderate to 2 large mismatched perfusion defects or the arithmetic equivalent in moderate or large and moderate defects
- Single matched ventilation-perfusion defect with a clear chest radiograph
- Single ventilation-perfusion matches are borderline for “low probability” and thus should be categorized as “intermediate” in most circumstances by most readers, although individual readers may correctly interpret individual scintigrams with this pattern as “low probability”
- Difficult to categorize as low or high, or not described as low or high.
Low Probability
- 0-19% likelihood for PE
- Perfusion defects matched by ventilation abnormality provided that there are: (a) clear chest radiograph and (b) some areas of normal perfusion in the lungs
- Extensive matched V/Q abnormalities are appropriate for low probability, provided that the CXR is clear
- Any perfusion defect with a substantially larger chest radiographic abnormality
- Any number of small perfusion defects with a normal chest radiograph
- Nonsegmental perfusion defects (e.g., cardiomegaly, enlarged aorta, enlarged hila, elevated diaphragm)
- Multiple matched V/Q abnormalities, even when relatively extensive, are low probability for PE
- The prevalence of PE in patients with extensive matched V/Q defects and no CXR abnormality was 14% (low probability)
Normal
- No perfusion defects or perfusion exactly outlines the shape of the lungs seen on the chest radiograph (note that hila and aortic impressions may be seen and the chest radiograph and/or ventilation study may be abnormal)
Defect Descriptors, Identified in Studies Other Than PIOPED
- “Segmental Equivalent” Sizing: The moderate segmental defect is counted as 0.5 of a large segmental defect (two moderate sized segemental defects are therefore equivalent to one large segmental defect). All moderate and large defects can be than added up to result in total segmental equivalent units. (Example: 3 moderate segmental defects and 1 large = 2.5 segmental equivalents)
- “Stripe Sign”: A thin line (stripe) of activity (perfusion) at the pleural surface of a perfusion defect. The finding is associated with underlying emphysema and is likely related to spared perfusion in the cortex of the lung. In the PIOPED study only 7% with a stripe sign actually had a pulmonary embolism corresponding to that segment. Hence, in the absence of other perfusion abnormalities, the finding is considered low probability for PE. In cases in which there is a high clinical concern for pulmonary embolism, SPECT images may help to better define the defect.
- “Triple Match”: A matching perfusion, ventilation, and CXR abnormality is referred to as a “triple match”. The overall prevalence of PE in all lung zones with triple matches was 26% in the PIOPED population. There were no significant differences between the size of the matching V/Q defects and chest radiographic opacities and the prevalence of PE. The prevalence of PE in small regions (less than 25% of a zone) with triple matches was 27%, compared with 21% in large regions (over 75% of a zone) with triple matches. However, there was a difference in prevalence of PE between lung zones- pulmonary embolism was significantly more common in lower lung zone triple matches (upper - 11%; middle - 12%; lower - 33%). Pulmonary embolism was significantly more common in lower lung zone triple matches. Therefore, a triple-match in the upper or middle lung zones is considered low probability for PE, but a triple-match in the lower lung zone should be interpreted as intermediate probability.
Xe 133
- inhaled
- single breath, equilibrium, washout
Tc DTPA
- must do before MAA
Tc MAA
- 70-500K particles
- free tec - thyroid, kidneys
- R → L shunt - brain, kidneys
- abnl abd uptake - shunt, free tec, or small particle size
Renal
Tc DMSA
- cortical agent
- pyelo, cyst, abscess, scar, berthin
- indications:
- first UTI
- mass vs. column of berthin
Mag 3
- 10 mCi
- Lasix 10mg
- no excretion first 2 min
- tubular agent
- on a transplant study, look for → thrombosis, leak, obstruct
- normal values:
- time to peak = 2-4 min
- half life <10 min
- 10-20 min = indeterminate
- >20 min = abnormal
- split renal fxn
- normal = 43-50%
- borderline = 40-43%
- minimum clinically significant interval change = 6%
Captopril renography
- renovascular HTN
- threshold is 20% asymmetric decline in function
Cardiac
General
- Coronary artery dominance
- PDA arises from:
- RCA = right dominant (most common)
- LCX = left dominant
- DDx right ventricular uptake is RVH or R heart strain
Interpretation
- High-risk
- Large perfusion defect on stress imaging
- Multiple coronary artery territories
- Large reversibility
- Increased lung upake
- Transient LV dilitation
- Low-risk
- Normal stress images
- Small stress defect
- Small reversibility
- Look for extracardiac activity
- Lung activity = sign of extensive CAD and poor prognosis
- Lung nodule
- Parathyroid adenoma
Transient Ischemic Dilitation
- TID > 1.22 is abnormal with exercise stress
- TID > 1.36 is abnormal with physiologic stress
Exercise Stress
- Bruce protocol (3 min stages, increasing speed and incline)
- 12 lead EKG
- insert IV
- stop for drop in BP, v tach, chest pain, ST depression, or patient unable to continue (last 3 are relative)
- don't stress patients with aortic stenosis, L main disease
- Satisfactory Effort
- 85% max predicted hr
- double product >25,000 (product of HR x SBP)
Adenosine
- 140 ug/kg/min
- 6m infusion, inject @ 3m
- contraindications - bronchospasm (COPD/asthma), heart block, SA node disease
- aminophylline
- Adenosine induced heart block
- d/c adenosine (half life in range of seconds, so heart block will break)
- restart with lower dose (heart block is dose dependent) and complete the study
Dobutamine
- 6m min
- contraindications - MI, HTN
MuGA
- most accurate LVEF
- nl > 50%
- <45% EF is bad, decreasing EF to this level means stop therapy
- EF = (EDV - ESV) / (EDV - background)
- place background in lung next to LV or possibly in stomach
- background over spleen NOT okay - overestimates EF
- 24 frames per r-r interval
Miscellaneous
Tc RBC
Labeling Technique
- In vivo
- stannous pyrophosphate is administered intravenously, followed in 15-30 minutes by 99mTc pertechnetate
- Modified in vivo
- stannous pyrophosphate is administered intravenously
- 15-30 minutes later, 3-5mL of blood is withdrawn into a shielded syringe containing 99mTc pertechnetate and an anticoagulant
- blood is incubated for 10 min (agitating periodically) and then infused
- In vitro
- blood is withdrawn and placed in a closed vial containing stannous chloride and sodium hypochlorite (oxidizes excess extracellular stannous ion and prevents extracellular reduction of 99mTc pertechnetate)
- 99mTc pertechnetate is added and labeling occurs during a 20 minute incubation and injection
- hemangioma, blood vol, MUGA, GI bleeding
- criteria for GI bleed - not present @ beginning, increased act, movement
Free pertecnetate
- activity in stomach, kidney, thyroid, salivary glands, choroid, bladder
- Meckel's scan
- increased activity over time paralleling activity in stomach
One-liners
- Honda sign = sacral insufficiency fx
- Kasai procedure done w/i 3 months age
- Gastrinomas usually located in small bowel or pancreas
- Think EG for cystic bone lesions with a normal bone scan (they can be hot, too) or myeloma/lymphoma
- Increased uptake in one hand, think radial artery injection
- When shown myositis ossificans, also think of a parosteal osteosarcoma
- Interstitial lung dz can have hot lung bases on MDP
Differentials
Hot mets on bone scan
- Mucinous adenoCA
- Other adenoCA
- MDP goes to areas of cell death
Cold defect on bone scan (HM RANT)
- Hemangioma/Histiocytosis (EG)
- Myeloma/Plasmacytoma
- RCC
- Anaplastic (aggressive) tumors
- Neuroblastoma
- Thyroid CA
- AVN, XRT, cold osteo
Superscan
- Metabolic
- Renal osteodystrophy
- Osteomalacia
- randomly distributed focal sites of intense activity (Looser zones/pseudofractures)
- Hyperparathyroidism
- focal intense uptake corresponds to site of brown tumors
- Hyperthyroidism
- rate of bone resorption more increased than rate of formation
- Widespread bone lesions
- Diffuse skeletal metastases
- prostate, breast, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, lung, bladder, colon, stomach
- Myelofibrosis/myelosclerosis
- Aplastic anemia, leukemia
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
- Systemic mastocytosis
- Widespread Paget disease
One Lung Absent Perfusion
- hilar mass
- pulmonary artery agenesis
- unilateral PE
- Swyer-James (will have poor ventilation, too)
Increased MDP Soft Tissue Uptake
- lymphedema
- venous obstruction
- RSD
- infection (cellulitis)
Focal Increased MDP Three Phase Activity
- osteomyelitis
- fracture
- AVN
- surgery (osteotomy)
- primary or secondary neoplasm
- osteoid osteoma
- RSD (Uptake involves entire extremity. 50% of patients have increased blood flow and blood pool uptake, while 95% have increased uptake on delayed images.)
- charcot joint
- severe osteoarthritis
Increased Cortical MDP Uptake
- hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
- renal osteodystrophy
- vitamin A intoxication
- fluorosis
- thyroid acropachy
- manifestation of grave's disease
- melorheostosis/Englemann's
- pachydermoperiostosis
- idiopathic, familial hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
Monoarticular Arthritis
- Gout, PVNS, TB, septic arthritis
Young Child w/ Hot Lesion on bone scan
- neuroblastoma (95% are hot since 95% calcify)
Diseases
Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB)
- second most common senile dementia (after Alzheimer's)
- Lewy bodies = eosinophilic structures w/i neurons
- overlap with Alzheimer's - may be difficult to dx clinically
- FDG-PET shows diffuse glucose hypometabolism, particularly in the occipital region
Artifacts
- off-peak flood - every other PMT lights up
Quality Control
Gamma Camera QC
Peak
- daily and with each new RP
Flood
- daily, <5% uniformity
- intrinsic no collimator
- extrinsic with collimator
Linearity and resolution
- weekly with bar phantom
Field Uniformity and Center of Rotation
- monthly
Spect QC
Flood
- uniformity < 1%
COR and detector malalignment
- ring and comet tail artifacts on axial recons
Motion
- sinogram
- summed projection
- cine
Attenuation
- evaluation cine images for evidence of attenuation
- attenuation correction may introduce artifacts
PET QC
Check scan (blank)
- daily
Bucket setup
- when system is drifting
2D and 3D normalization
* weekly to monthly or after bucket setup
Phantom calibration
* on new 68Ge phantom
Dose Calibrator QC
- All doses must be measured prior to administration and be within 10% of prescribed dose
- Isotopes used for dose calibrator QC include 57Co, 99mTc, 133Ba, 137Cs
Constancy
- 137Cs, daily
- reproducibility in measuring a constant source over a long period of time
Channel Check
- 137Cs, daily
Linearity
- quarterly
- ablility of calibrator to indicate the correct activity over the range of use of that calibrator
Accuracy
- annually
- for a given calibrated reference source, the indicated millicurie value is equal to the millicurie value determined by the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) or by the supplier who has compared that source to a source that was calibrated by the NBS
- at least two sources with different principal photon energies (such as Co-57, Co-60, or Cs-137) should be used; one must have a principal photon energy between 100 keV and 500 keV
Geometry
- checked at installation
- indicated activity does not change with volume or configuration
Radiopharmaceutical QC
Sterility
- pyrogens detected with limulus test
Chemical Purity
- < 10 µg/ml Al3+ in 99mTc eluate
Radionuclide Purity
- 0.15µCi of 99Mo / 1.0 mCi of 99mTc
Radiochemical Purity
- free 99mTcO4-, reduced 99mTcO2, tin colloids
- reduced and tin colloids localize to RES
NRC Guidelines
- authorized user - may order, receive and inject isotopes
- protocol
- identify patient → 2 forms of ID (name and birthdate)
- confirm order
- have pt state ID and procedure they're supposed to have
- informed consent
- written directive analagous to prescription for therapy
Radiation Safety
Decay Mechanisms
- isomeric transition (99mTc → 99Tc + )
- 99mTc
- positron (+) decay
- 18F, 15O, 13N, 11C, 68Ga
- generally high radiation dose
- negatron (-) decay
- 131I and 133Xe diagnostic, 32P, 90Sr, 90Y therapeutic, also 99Mo
- generally highest radiation dose
- electron capture
- 67Ga, 111In, 123I, 201Tl
Common radionuclides
| t½ | keV | |
|---|---|---|
| 99mTc | 6h | 140 |
| TcO4-, Mibi, RBCs, SC, | ||
| Mag-3, DTPA, DMSA, ECD | ||
| 201Tl | 3d | 80 |
| Tl Chloride | ||
| 111In | 3d | 173, 247 |
| WBC, octreoscan, DTPA | ||
| 67Ga | 3d | 100,200,300,400 |
| Ga citrate | ||
| 123I | 13h | 159 |
| iodide, MIBG, NP59 | ||
| 131I | 8d | 364 + - |
| iodide, MIBG, NP59 | ||
| 133Xe | 5d | 81 |
| Xe gas | ||
| 18F | 110m | 511 |
| FDG |
Decay properties
t½
- 7 half lives < 1 % of original activity
- 10 half lives < 0.1 %
inverse square law
- dose 1 / d2
HVL and TVL (shielding)
Gamma Camera
Gamma camera
collimator, crystal, PMT, preamplifier, amplifier, CPU
Collimators
- resolution increases with
- increased collimator thickness
- decreased collimator hole diameter
- decreased patient to collimator distance
- parallel hole
- low, medium, or high energy
- general purpose or high resolution
- pinhole
- small parts, magnification, high resolution
- converging hole → small FOV, magnification, increased resolution
- diverging hole → large FOV, minification, decreased resolution
- resolution inversely proportional to sensitivity
99Mo - 99mTc Generator
- Reactor produced
- 99Mo → 99mTc → 99Tc → 99Ru
99Mo Breakthrough Test
- NRC limit = 1.00 mCi 99Mo / mCi 99mTc
- USP limit = 0.15 mCi 99Mo / mCi 99mTc
Aluminum Ion Breakthrough
- Al3+ degrades image quality
- NRC limit = 20mg per mL of eluate (thermal generator)
- = 10mg per mL of eluate (fission generator)
- measured by colorimetry on filter paper
Radiation Interaction with Matter
photoelectric effect
- complete absorption of with expulsion of e- with charactersitic X-rays
internal conversion
- completely absorbed by originating atoms e- shell with characteristic X-ray production
Compton scatter
- deflection of with loss of energy and nuclear excitation with characteristic X-rays production
+
annihilation
- + + - → two 511keV rays at 180 degrees
- and -
ionization
- characteristic X-rays
Exposure, Dose, Dose Equivalent
- Bq = 1 dps
- 1 mCi = 37 MBq
| SU | IU | |
|---|---|---|
| X = Q/m | R | C/kg |
| D = E/m | 100 rad | Gy |
| DE = D x Q | 100 rem | Sv |
Occupational Dose Limits
| Background | 0.3 rem / y |
| Whole body | 5 rem / y |
| Lens | 15 rem / y |
| Extremities / skin / organ | 50 rem / y |
| Cumulative dose | 1 rem x age |
| Fetus | 0.5 rem / 9 m 0.05 rem / m |
| General population | 0.1 rem / y |
Women, Pregnancy, and Lactation
In women of childbearing age:
- check -HCG
- elective NM exams within 10 d of start of menses
- MD approval required (consent)
- fetal dose for rad workers 0.5 rem / 9 mo
- negligible dose < 10 rem
For lactating females, stop breastfeeding:
- 99mTc label → 24 hr
- 67Ga, 201Tl → 2+ wks
- 131I → stop breastfeeding
Radiation safety general concepts
ALARA
- as low as reasonably achievable
- non-threshold, linear dose-effect relationship
- distance, time, shielding
Stochastic
- dose proportional to risk of effect
- cancer / gene mutations
Non-stochastic
- threshold required before effect
- acute radiation syndrome, cataracts, sterility
Receipt of Radioactive Materials
- Survey package within 3 hr of arrival
- Geiger counter
- 3 levels, highest allowed = 100 mrem/hr @ surface, 3 mrem/hr @ 1 m
- confirm with wipe test
- needs to be less than 2200 DPM / 100 cm2
- If elevated, notify NRC / state licensing agency and the package carrier, decontaminate or isolate package as necessary
Radiation surveys
Daily Monitoring
- hot lab, imaging rooms, radioassay lab, thyroid room
Spills
- If t ½ < 65 d, can use DIS (decay in storage), await background levels
- 10 half lives gives <0.1% of original radioactivity
Minor spills
- <1 mCi 131I or <100mCi 99mTc, 201Tl, 67Ga
- secure area, survey people and clothes, contain spill
- clean up area and place soiled material in plastic bags
- incident report by RSO after cleaning
- resurvey area
- liquid iodide is volatile and may require special clean-up
- consider Lugols for exposed staff
Major spills
- warn workers, isolate area
- summon RSO who directs decontamination
- immediate assessment of type and extent of spill, warning signs
- initiation of medical care as indicated
- decontaminate workers remove clothing, shoes, etc, shower and eye flush
- clean area, waste placed in heavy plastic bag in shielded container
Misadministration of Radiopharmaceuticals
Medical event = recordable event
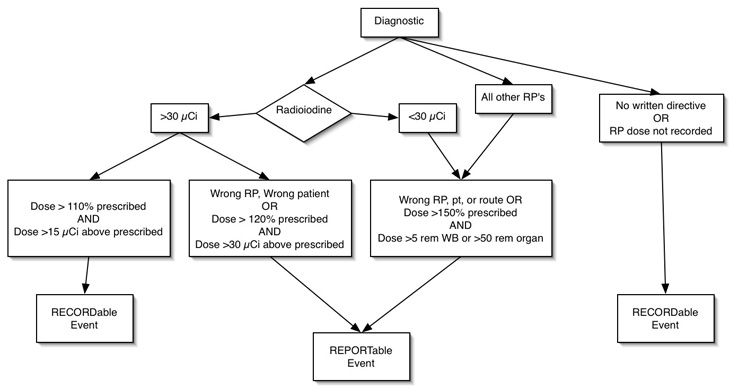
Diagnostic Misadministration
- RP without written directive when required
- RP with written directive where administered RP dose is not recorded
- 123I, 125I, 131I as NaI > 30 µCi if
- dose > 110% prescribed, and
- dose exceeds prescribed by 15 µCi
Reportable Events
- Incident report filed by RSO and retained for 3 years.
- NRC / State licensing agency, referring MD, and patient (guardian) notified within 24 hours by phone, letter to NRC within 15 days.
- Incident report by RSO, address in RSC meeting, retain record for 20 yrs
Diagnostic Misadministration
- Radioiodine > 30 µCi
- wrong patient or wrong RP, or
- dose > 120% prescribed dose and difference exceeds 30 µCi
- Radioiodine doses < 30 µCi and all other radiopharmaceuticals
- wrong patient, wrong RP, wrong route, or dose exceeds 150% of that prescribed, and
- dose > 50 rem to organ, or > 5 rem to whole body
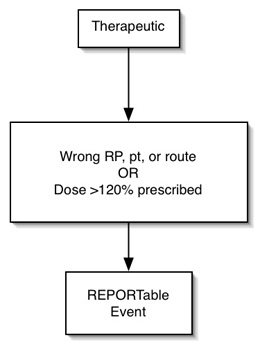
Therapeutic Misadministration
- Wrong patient, wrong RP, or wrong route, or
- dose > 120% of prescribed dose
I-131 Therapy
Before Therapy
- No IV contrast for at least 6? wks
- D/C synthroid 6 wks prior to therapy and start cytomel
- D/C cytomel 2 wks prior to therapy
- D/C PTU and methimazole 3 days before therapy
- Low iodine diet 1 wk prior to therapy
- 1-2 days prior to therapy, obtain labs
Precautions
- Always wash your hands with soap and water after you use the bathroom. Dry your hands thoroughly with a towel that only you are using
- Separate all towels, washcloths, and bed linens. Wash all of these items separate from the family wash
- In order to dilute the amount of radiation in urine and feces, always flush the toilet at least two or three times after using the bathroom
- Wash the bathroom sink, shower, bathtub and bidet after each use
- Separate your plates, silverware and drinking cups. Better yet, use paper plates and plastic cutlery, so you won't have to wash your dishes separately from the rest of the family
- If you are cooking for the family, remember not to taste any of the food with a spoon that will be used for food preparation. Once it touches the saliva in your mouth it is considered to be contaminated and must be washed separately
- Sleep in a separate bed from your partner. Avoid open mouth kissing and all sexual contact
- Radiation exposure is directly related to the amount of time you spend with another person as well as how intimate and close your contact is with them. Avoid prolonged intimate physical contact with babies, children and pregnant women. You may perform all essential duties such as changing diapers, if no one else is available to help you. Wash your hands before and after these tasks
- In order to flush out the radiation faster, keep yourself well hydrated (preferably with water) so that the radioactive iodine will be passed out of your body through your urine.
- These precautions should be followed for three days after the I131 test
Clearance for discharge after therapeutic administration
Contacts must receive < 500 mrem total body dose
- dose estimated by t ½ , expected duration of contact, and distance of contact
Transportation
- home from clinic / hospital
- highest dose rate
Close contacts
- shared bed
- longest exposure time with high dose rate
Casual contacts
- workplace, shared living space
dokuwiki\Exception\FatalException: Allowed memory size of 134217728 bytes exhausted (tried to allocate 20480 bytes)
An unforeseen error has occured. This is most likely a bug somewhere. It might be a problem in the authplain plugin.
More info has been written to the DokuWiki error log.