ob_gyn
Table of Contents
GYN
Ovaries
- functional cysts – follicular cysts and corpus luteal cysts
Polycystic Ovaries
- enlarged ovaries
- echogenic stroma
- cysts in periphery (>5 cysts over 5mm in size)
- treated w/ clomiphene
Stein-Leventhal
- PCO, obesity, infertility / amenorrhea, and hirsutism
Hemorrhagic Cysts
- fine reticular septations or heterogeneous mass w/ multiple echoes
- high on T1 and homogeneously bright on T2
- resolves spontaneously (f/u 6-8 wks)
- ddx: endometrioma, hemorrhagic corpus luteum cyst, dermoid, follicular cyst
Ovarian Teratomas
- most common benign ovarian neoplasm
- classic mimicker
- rarely malignant
- at risk for torsion
- complex, partially cystic, w/ echogenic areas that may shadow
- dermoid plug = Rokitansky nodule
- presence of struma ovarii can (rarely) cause thyrotoxicosis
Benign Ovarian Neoplasms
- mucinous or serous cystadenomas, Brenner tumors
- granulosa cell tumors, fibromas, thecomas (secrete estrogens –> endometrial hyperplasia)
- Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors (secrete androgens –> virilization)
- cannot differentiate from malignant neoplasms
- complex lesions with septations and solid tumor nodules
- RI > 0.4 (not reliable)
Adnexa
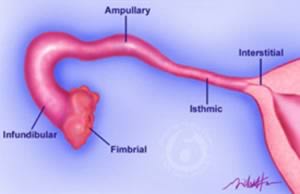
- ovary, fallopian tube, and broad ligament(contains fallopian tube and uterine artery)
- fallopian tube segments – intramural, isthmus, ampulla, and infundibulum
- isthmus is narrowest segment
Adnexal Mass
- benign or malignant ovarian tumor
- cystic teratoma
- pedunculated fibroid
Cystic Adnexal Mass
- hydrosalpinx
- cystic teratoma
- corpus luteum cyst
- benign or malignant ovarian tumor
Ovarian Malignancy
- solid nodules, thick septations, irregular wall, poorly defined margins
- RI < 0.4 and PI > 1
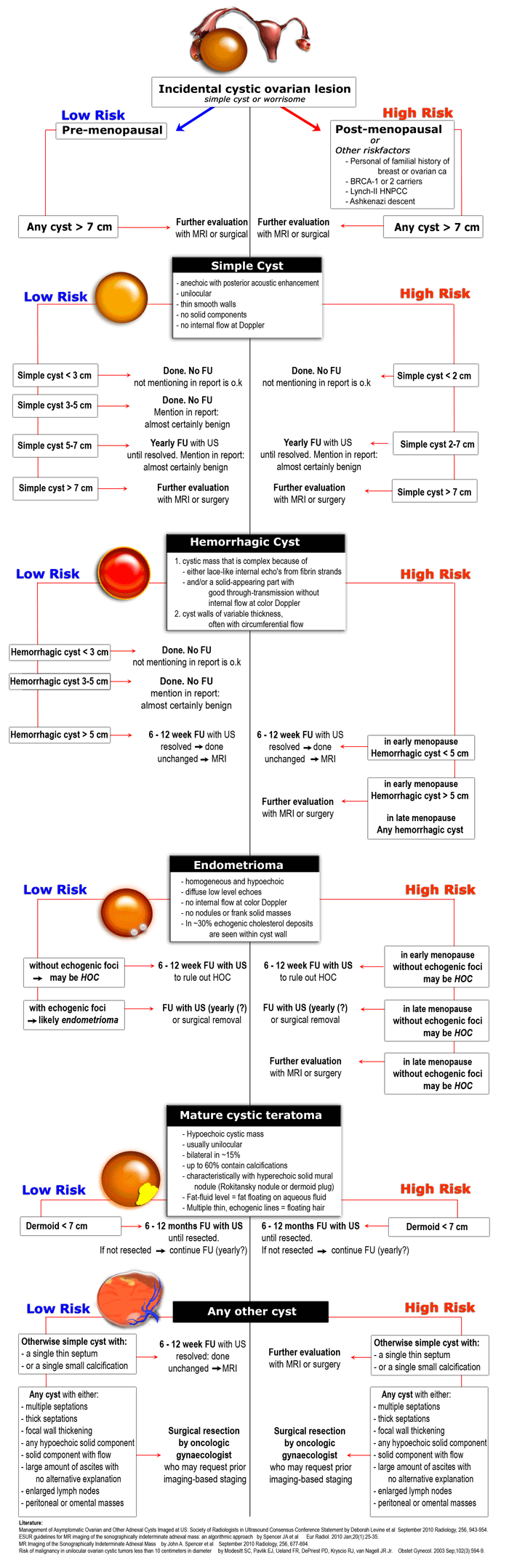
Guidelines
- Premenopausal:
- <2.5cm and simple – Physiologic follicle. No follow up
- 2.5cm to 10cm (simple or complex) – Follow up in 6 weeks x 2
- >10cm – Laparoscopy and resection
- Postmenopausal:
- <5.0cm and simple – Follow up in 3 months, then 6 months x 2, then 1 year
- >5.0cm or complex at any size – Laparoscopy and resection
Uterus
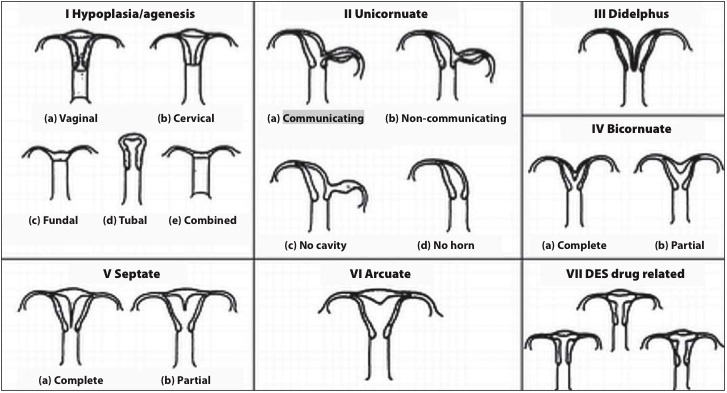
Congenital Anomalies
Endometrium
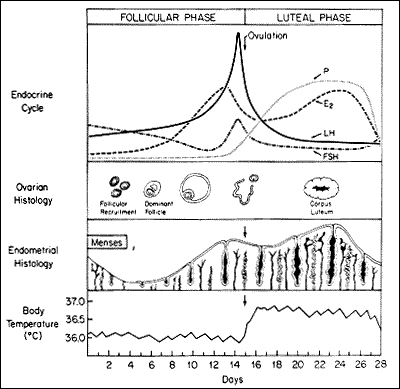
- two layers – basal layer and functional layer(shed during menstruation)
- atrophies after menopause, which may lead to bleeding
Endometrial thickness
Premenopausal
- menstrual: 2-4 mm
- proliferative: 5-11 mm
- secretory: 7-16 mm
Postmenopausal
- Will depend on the whether or not there is a history of vaginal bleeding, and on the use of hormonal therapy / tamoxifen.
- Vaginal bleeding (and not on tamoxifen):
- suggested upper limit of normal is <5 mm
- the risk of carcinoma is ~7% if the endometrium is >5 mm and 0.07% if the endometrium is <5 mm
- on hormonal replacement therapy: upper limit is 5 mm
- No history of vaginal bleeding:
- the acceptable range of endometrial thickness is less well established in this group, cut-off values of 8-11 mm have been suggested
- the risk of carcinoma is ~7% if the endometrium is >11 mm, and 0.002% if the endometrium is <11 mm
- If on tamoxifen: <6 mm (although ~50% of those receiving tamoxifen have been reported to have a thickness of >8 mm)
After D&C or spontaneous abortion, endometrium should be no thicker than 5 mm or suspect retained POC
Endometritis
- ultrasound is nonspecific
- may see endometrial fluid, debris, gas
- caused by PID, postpartum, postinstrumentation, IUD
Endometrioma / Endometriosis
- adnexal cyst filled with homogeneous low-level echoes (“ground glass” appearance) or reticular septations, similar to hemorrhagic cyst
- bright on T1 w/ low signal areas on T2 (shading) due to iron
- may be multilocular with areas of anechoic fluid or may have fluid-fluid levels
- often multiple
- associated w/ metrorragia, dysmenorrhea, infertility
- cyclic Δ
Endometrial Polyps
- can cause intermenstrual beeding, menorrhagia, or infertility
- saline infusion sonohysterography is useful
- homogeneously hyperechoic or complex with cysts
- single feeding vessel on color doppler
- treated hysteroscopically
Endometrial Hyperplasia
- present w/ vaginal bleeding
- diffuse process, w/ or w/o cellular atypia
- if atypia present, there is a substantial risk of progression to endometrial CA
Endometrial Carcinoma
- endometrial thickening (>8-10 mm) with an ill-defined endometrial-myometrial interface
- SIS: poorly distensible uterine cavity lined by a diffusely irregular and thickened endometrium or focal area of endometrial thickening
Myometrium
- hypoechoic
- atrophies after menopause
- bounded by endometrium centrally and serosa peripherally
Fibroids
- three types: intramural (confined to myometrium), submucosal (projecting into endometrium), and subserosal (projecting from serosal surface)
- color doppler will identify vessels
- have increased risk of pregnancy loss
- may cause pain during pregnancy
- may obstruct vaginal delivery
- may cause placental abruption or IUGR
- leiomyosarcomas enlarge over time
- dx of submucosal fibroid may be aided w/ sonohysterogram
- heterogeneous appearance due to:
- necrosis
- calcification
- cystic degeneration
- hyalinization
Adenomyosis
- Form of endometriosis where there is aberrant endometrial tissue in the myometrium
- Diffuse or focal
- US - Sonographic appearance overlaps w/ fibroids, but presence of small cysts or hypoechoic areas or variation during menstrual cycle is suggestive of adenomyosis.
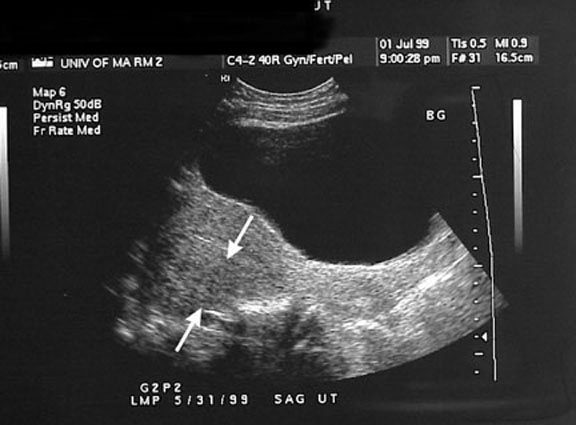
- Irregular, myometrial, cystic spaces predominantly involving the posterior uterine wall, an enlarged uterus with a widened posterior wall (see Image 1), an eccentric endometrial cavity, and decreased uterine echogenicity without lobulations, contour abnormality, or mass effects (which is more commonly seen with leiomyomas). Sonograms may also show an ill-defined margin between the normal myometrium and the abnormal myometrium, as well as an elliptically shaped myometrial abnormality.
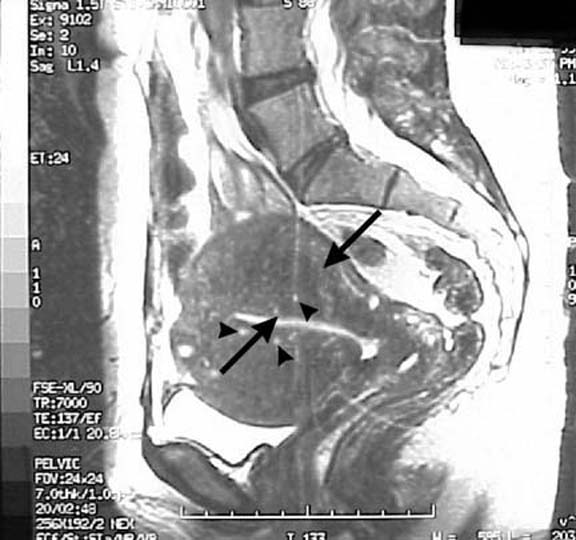
- MRI - Junctional zone thickness was 12 mm or greater. A maximum thickness of 8 mm or less usually excludes the disease. When the maximum junctional zone diameter is 8-12 mm, secondary findings such as high–signal-intensity foci on T1- or T2-weighted images, are necessary to make the diagnosis.
- on HSG will appear as small diverticula of the body or fundus of the uterus as opposed to SIN, which appears as small diverticula of the isthmic portion of the fallopian tubes
Nabothian Cyst
- within cervix
Cervical Cancer
- typically SCC
- cervical stenosis with endometrial fluid collection
- parametrial invasion
- irregular, poorly defined margins of lateral cervix
- prominent ST stranding
- obliterated fat planes
Cervical Cancer Staging
- Stage 1 - confined to cervix
- Stage 2 - beyond cervix, but not to pelvic sidewall or lower 1/3 of vagina
- 2A - vaginal invasion (upper 2/3)
- 2B - parametrial invasion
- Stage 3 - extends to lower 1/3 of vagina
- 3A - lower 1/3 of vagina
- 3B - pelvic sidewall
- Stage 4 - see below
- 4A - bladder or rectal invasion
- 4B - distant mets (typically lung and liver)
Hydrosalpinx
- caused by PID, endometriosis, prior instrumentation, leading to adhesions that obstruct the peritoneal opening of the tube
- infected = pyosalpinx
Tubo-Ovarian Abscess
- severe form of PID, usually bilateral
- complex, multiloculated adnexal mass w/ echoes from debris/pus
- may have thick septations, ovary may be encased
Ectopic pregnancy
- tubal, cornual, cervical, and intraperitoneal
- increased peripheral blood flow
- “tubal ring” = echogenic ring
- cornual = intramural portion of fallopian tube
- blood or secretions in uterus = pseudogestational sac
- heterotopic = coexistence of ectopic and intrauterine pregnancies
- beta levels should double every 2 days
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- complete hydatidiform mole – large amount of trophoblastic tissue w/ absence of fetal tissue – 46XX, both sets from father
- appears as large complex mass with cystic spaces surrounded by echogenic tissue
- partial mole – both fetal (usually dead or abnormal) and abnormal placental tissue are present – typically triploid (69 XXY)
- appears as gestational sac containing abnormal fetus and markedly thickened placenta w/ focal cystic areas, may mimic hydropic placenta w/ fetal demise
- trophoblastic tumor – rare, develops in placental bed following normal pregnancy, appears similar to recurrent or persistent complete moles (poorly defined mass or masses in the uterus, with hypoechoic areas that represent vessels)
- choriocarcinoma – develops infrequently after molar evacuation
DIFFERENTIALS
Cystic Abdominal Mass (fetus)
- mesenteric or omental cyst
- ovarian cyst or teratoma
- enteric duplication cyst (assoc spinal or GI malformations)
- meconium pseudocyst
- MCDK
- PUV w/ urinoma
- urachal cyst
- obstructed bowel loop
IUGR (dates mismatch = IUGR)
- maternal – deficient supply of nutrients: smoking, malnutrition, multiple gestations, anemia, high altitude, maternal vascular disease, severe diabetes
- placental – extensive placental infarctions, chronic partial separation, placenta previa
- fetal – decreased intrinsic growth, congenital heart disease, genitourinary anomalies, CNS anomalies, chromosomal abnormalities (trisomy 13, 18, 21), viral infection (rubella, CMV)
- symmetric = severe, early onset, fetal causes such as chromosomal abnormalities
Endometrial Mass & Positive ß-hCG
- retained POC
- endometritis
Endometrial Fluid
- cervical stenosis
- cervical CA
- hydrometrocolpos
- endometritis
Pelvic Free Fluid
- separate into gynecologic and non-gynecologic etiologies
Placental Lesions
- infarct (maternal side)
- intervillous thrombus
- fibrin deposition
First Trimester Vaginal Bleeding
- spontaneous abortion
- ectopic pregnancy
- anembryonic pregnancy
- molar pregnancy
- subchorionic hemorrhage
OB - General
- Follicle ruptures at 20-24mm
- Sac diameter grows 1.13mm/day
- Normal gestational sac ~2x length of embryo
- Yolk sac should be seen w/ 8-10mm gestational sac or at 5-6 wks (transvaginal)
- Fetal pole should be seen w/ 18mm gestational sac (25mm is diagnostic)
- Fetal heart activity seen at 6w2-3d (CRL ≥ 5mm)
- Cervical length should be >3cm
- Corpus luteum regresses by 16-18 wks
- Need to be 14wks GA to dx oligo in setting of renal agenesis (Potter syndrome)
- Ventricular atria should be < 10mm
Should see gestational sac by:
- 1000 IU (transvag)
- 1800 IU (transabdominal)
Fetal Heart Rate
- 5-6 wks → 100-110
- 8-9 wks → 150-170
Fetal Demise
- f/u study in 1wk – two studies need to confirm before D&E
Amniotic fluid measurements
- Subjective
- Single-deepest pocket measurement - measured vertically, normally between 3-8cm
- Four quadrant AFI - sum of deepest vertical pocket in each quadrant, normally 5-20cm
Fetal measurements
- CRL 6-13 wks (most accurate)
- Femur length 14+wks, best >26wk
- BPD 2nd trimester
Macrosomy
- >4,000 grams
- > 90th percentile
- associated w/ obesity and diabetes
- can be seen with incorrect dating
- Complications:
- oligohydramnios
- shoulder dystocia
- C-section / prolonged labor
- structural abnormalities
- meconium aspiration
Early Pregnancy Loss/First Trimester Pregnancy Failure
- No cardiac activity on TVS (w/ embryo >5mm in length or GA at least 6.5 weeks)
- Suspicious, but not diagnostic:
- Mean sac diameter of more than 8 mm and no visible yolk sac
- Mean sac diameter of more than 16 mm and no visible embryo
- ß-HCG above 1,000 mIU/ml and no gestational sac seen
- ß-HCG above 10,000 mIU/ml and no embryo identified
Normal Yolk Sac (5-6 wks)
- Round
- <5-6 mm
- anechoic
- thin wall
- no calcifications
Slow Embryonic Heart Rate
- At 6-6.3 wks (CRL<5mm), <100bpm assoc with increased risk of fetal demise; if <90, rec f/u in 1-2 wks
- At 6.3-7 wks (CRL 5-9mm), <120bpm assoc with increased risk of fetal demise; of <110, rec f/u in 1-2 wks
Subchorionic Hematoma
- blood coll b/w chorion and uterine wall
- thick irregular membrane, may track beneath placenta, may have internal echoes
- prognosis related to size of hematoma
- differentiate b/w normal fluid b/w chorion and amnion
- tx is bedrest
Marginal Cord Insertion
- within 2cm of edge
Velamentous Cord Insertion
- aberrant vessels traveling between chorion and amnion
- risk of bleeding during labor, preterm labor, fetal anomalies
Placenta Previa
- placenta covering the internal cervical os
- complete, partial, or marginal
- can resolve
- necessitates C-section
Vasa Previa
- rare type of velamentous cord insertion in which umbilical vessels cross the internal os
- vessels connecting separate succenturiate lobe to main portion of placenta
- cord vessels of velamentous (membranous) cord insertion from low-lying placenta
- aberrant chorionic vessels in association with marginal cord insertion from low lying placenta
- complications:
- bleeding from torn fetal vessels
- cord compression by presenting part during labor
- cord prolapse
- 50-100% risk of fetal mortality
Placental Abruption
- premature detachment of placenta from uterine wall
- retroplacental or subchorionic hematoma
- normal u/s does not r/o abruption
Placenta Accreta, Increta, Percreta
- accreta: attachment of the placenta directly to the myometrium, without invasion of chorionic villi into the myometrium
- increta: invasion of chorionic villi into the myometrium
- percreta: penetration of villi through the myometrium, to or through the serosa of the uterus
- frequently occur @ site of prior C-sect
- raise possibility when 1) anterior previa seen w/ prior c-section and 2) u/s shows thinning of myometrium overlying placenta (1-2 mm or less)
Succenturiate Lobe
- accessory placental lobe
- failure of placental villi to atrophy
- can lead to hemorrhage prenatally or during labor
- can lead to postpartum hemorrhage if not delivered
Chorioangioma
- benign placental tumor
- cause fetal growth restriction & hydrops
- solid mass within or projecting from placenta
- may cause high-output heart failure (distended umbilical vein) and hydrops
Cervical Incompetence
- early dilitation of cervix
- shortening and funneling of cervix
- length: 3cm normal, 2.5-3cm borderline, <2.5cm incompetent
- complication is pre-term labor
- treatment is cerclage
Uterine Synechia and Amniotic Sheet
- uterine synechia result in amniotic sheets, smooth thick projections of tissue into the gestational sac
- broad based attachment to uterine wall
- does not adhere to fetus, therefore no fetal abnormalities
- increased incidence of fetal malpositioning
Oligohydramnios (DRIPPC)
- Demise of fetus, Drugs
- Renal anomalies, bilateral (agenesis, PCKD, obstruction)
- Potter syndrome - secondary deformities such as pulmonary hypoplasia, abnormal facies, clubfeet
- IUGR (decreased renal perfusion)
- PROM
- Post-dates, 40 wks or greater
- Chromosomal abnormalities
Polyhydramnios (TARDI)
- Twins
- Anomalies, fetal (esophageal, duodenal, small bowel obstruction, anencephaly, facial clefts/tumors, intrathoracic masses, mesoblastic nephroma)
- Rh incompatibility
- Diabetes
- Idiopathic
- associated with chromosomal abnormalities
- causes maternal symptoms (pain, premature contractions, LE edema, hydronephrosis)
Intra-amniotic Hemorrhage
- can be spontaneous, often with subchorionic hematoma or abruption
- may be iatrogenic (amniocentesis)
- no sequelae
- echogenic amniotic fluid
Single Umbilical Artery
- more common in multiple pregnancies
- associated with structural abnormalities (holoprosencephaly, hydrocephalus, cerebellar dysgenesis) and Trisomy 18
Umbilical Cord Cysts
- Allantoic duct cyst
- may be assoc w/ fetal abnormalities (such as omphalocele)
- Omphalomesenteric duct cyst
- Pseudocyst
- contains wharton's jelly
Twin pregnancy
- dizygotic = dichorionic (different sexes must be dizygotic)
- two placentas = dichorionic
- delta sign / twin peak sign (extension of placenta into base of membrane) = likely dichorionic
- membrane:
- thick membrane (>2mm) = likely dichorionic
- thin membrane (1-2mm) = likely monochorionic, diamniotic
- really thin membrane (<1mm) = likely monochorionic, monoamniotic
- two yolk sacs or two amnionic sacs = diamniotic
- intermingling of cords, no membrane = monoamniotic
Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome
- discrepant amniotic fluid volumes (severe = “stuck twin”)
- donor has anemia and IUGR
- recipient can have high-output cardiac failure, polycythemia, and hydrops
- discordant fetal size
- monochorionic placentation
Death of Twin
- dichorionic <10wks = vanishing twin
- dichorionic >10wks = partially resorbed
- monochorionic twin death leads to ischemic damage in co-twin (“twin embolization syndrome”)
OB - Neuro
Normal size of lateral vents
- 8-10mm
- form @ 7 wks and remain stable
Cisterna magna normally <10mm
S:D ratio
- starts <4 @ 26-30 wks
- <3.5 @ 30-34 wks
- <3 from 34 wks onward
- increased risk of perinatal morbidity and mortality
- absent or reversed end-diastolic flow is poor prognostic sign
- associated with placental insufficiency
Serum AFP measured @ 15-20 wks
- >2.5 MOM is abnormal, assoc with neural tube defects
- <0.5 MOM assoc w/ Trisomy 18/21
Triple/Quadruple Screen
- High AFP = neural tube defect or gastroschisis
- Low AFP = Down syndrome
- High hCG = Down syndrome
- Low Estriol = Down syndrome
- High Inhibin-A = Down syndrome
Hydrocephalus
- width of lat vent @ atrium >10mm
- “dangling choroid”
- ddx aqueductal stenosis, dandy-walker, myelomeningocele (Chiari), encephalocele, arachnoid cyst, intracranial tumor, intracranial hemorrhage
Choroid Plexus Cysts
- associated w/ Trisomy 18 & 21
- look for associated abnormalities
- correlate with maternal age, triple screen
Anencephaly
- absence of fetal cranium
- some dystrophic brain tissue may be seen
- active fetus w/ polyhydramnios
- prominent orbits with “frog-like” appearance
Dandy-Walker
- dandy walker cyst with keyhole shape, communicates w/ 4th ventricle
- dilated cisterna magna
- inverse relationship b/w chromosomal abnormalities and presence of hydrocephalus
Encephalocele
- secondary to neural tube defect, amniotic band syndrome, Meckel-Gruber syndrome
- elevated AFP
Holoprosencephaly
- lobar - incomplete falx, partially fused hemispheres
- semilobar - fused hemispheres, partially fused thalami
- alobar - worst, large central ventricle, fused thalami
- associated with Trisomy 13
Schizencephaly
- clefts
Agenesis of Corpus Callosum
- complete or partial, partial usually affecting posterior aspect
- parallel ventricles, colpocephaly
- sulci radiate from roof of 3rd vent
- cavum septum pellucidum excludes ACC
- associated with interhemispheric cyst
Intracranial Hemorrhage
- usually occurs post-natally, but can result from maternal drug abuse, thrombocytopenia, anticoagulation, trauma, also twin-twin transfusion, death of co-twin, fetomaternal hemorrhage
- may result in porencephaly & parenchymal loss
Hydranencephaly
- results from massive vascular accident
- absence of cortical tissue, fluid-filled fetal head
- falx IS present, differentiating from alobar holoprosencephaly
TORCH Infections
- findings include microcephaly, periventricular calcifications, hydrocephalus, cerebellar aplasia, encephalomalacia, porencephaly
Spina Bifida
- failure of posterior vertebral arches to close
- Chiari II virtually always present
- assoc with folic acid deficiency
- “lemon sign” – flattening or concavity of frontal bones in second trimester, returning to normal in third trimester
- banana sign – curved appearance of cerebellum, pulled into foramen
- associated anomalies – clubfoot, scoliosis/kyphosis
Hemivertebrae
- part or all of one side of vertebral body and posterior elements is absent
- associated with variety of syndromes
Scoliosis
- associated with hemivertebrae, arthrogryposis, neurofibromatosis, skeletal dysplasias
Arthrogryposis
- scoliosis, multiple limb contractures, hydrops
Caudal Regression and Sacral Agenesis
- both found in fetuses of diabetic mothers, particularly with poor glucose control
- caudal regression - spectrum of abnormalities involving lower spine, pelvis, and lower extremities
- sacral agenesis - absence of two or more sacral vertebrae
Sirenomelia
- agenesis of spine and pelvis
- single or fused lower extremity
- renal agenesis
- imperforate anus
Sacrococcygeal Teratoma
- may grow anterior or exophytically posterior
- may cause hydronephrosis
- may result in neurogenic bladder or lower extremity paralysis
- highly vascular → HOCHF → hydrops
Cleft lip
- may be assoc w/ holoprosencephaly if midline
- assoc w/ syndromes
- may have polyhydramnios from difficulty swallowing
Macroglossia
- assoc w/ diabetic mother, Beckwith-Wiedeman, fetus w/ hypothyroidism
Micrognathia
- hypoplastic mandible
- associated w/ Trisomy 13 & 18
- also may cause polyhydramnios
Hypotelorism/Cyclopia/Proboscis
- assoc w/ holoprosencephaly
OB - Chest
CCAM
- pulmonary mass w/ cystic and solid components
- can cause polyhydramnios
- Type 1: cysts > 2cm
- Type 2: cysts ~ 1cm <– associated with renal and GI anomalies
- Type 3: microscopic cysts
- large ones carry a poor prognosis
- ddx - sequestration (has doppler flow), CDH (paradoxical diaphragm motion, location of stomach above diaphragm, extends from below diaphragm)
Pulmonary Sequestration
- segment of lung with systemic blood supply
- echogenic mass
- color doppler showing flow from aorta
- can be subdiaphragmatic
Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Bochdalek vs Morgagni
- findings - heterogeneous mass, intrathoracic stomach, opening in diaphragm, peristalsis in thorax, paradoxical motion w/ respiration
- poor prognosis if: liver w/i thorax, small size of contralateral lung, hydrops
- lung/head ratio <1 = poor prognosis, 1.0-1.4 moderate, >1.4 excellent
Tracheal Atresia
- Large, echogenic lungs w/ inverted diaphragms
- May have hydrops
Neck/Mediastinal Teratoma
- Complex mass, predominantly solid
- Grow rapidly, may cause HOCHF/hydrops
Increased Nuchal Translucency
- measured at 11-14 weeks sagitally
- Associated w/ 45X (Turner), Trisomy 21, 13, 18
- should undergo amniocentesis or CVS
- upper limit of normal - 2.2mm @ 11wk, 2.8 @ 14wk
Thickened Nuchal Fold
- measured at 16-20 weeks axially
- associated with Trisomy 21
- 6mm or more is abnormal
Cystic Hygroma/Lymphangiectasia
- Uni/multiloculated SQ mass filled w/ lymph fluid
- Posterior neck is common location
- Can cover entire body (generalized lymphangiectasia)
- Associated w/ 45X (Turner), Trisomy 21, 13, 18
- May have oligohydramnios
Pleural Effusion
- Isolated or associated w/ hydrops
- Isolated are likely chylothorax (thoracic lymphatic dysplasia) - associated skin thickening around thorax
- karyotyping is advised (6% anomaly)
- may tx w/ thoracentesis or thoracoamniotic shunt
Hydrops
- At least two of the following: pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, ascites, SQ edema
- Immune hydrops- maternal ab crossing placenta and destroying fetal RBC's
- Non-immune- cardiac anomaly, lymphatic dysplasia, CCAM, diaphragmatic hernia, arrhythmia, anemia, chromosome abnormality, TORCH infection, teratomas, chorioangioma (placenta), idiopathic
OB - Cardiac
Focal Intracardiac Echogenic Focus (papillary muscle calcification)
- Marker for aneuploidy
- Look for other abnormalities; if none, recommend f/u
- seen in 3-4% of normal fetuses
Pericardial Effusion
- normal is up to 2mm in 2nd trimester
HLHS & Aortic Stenosis
- small or absent L ventricle
- caused by limiting flow to L heart (ie. aortic stenosis)
- poor prognosis
- aortic stenosis may result in myocardial fibroelastosis - poor LV contractility
HRV & Pulmonic Stenosis
- small or absent R ventricle
- caused by pulmonic or tricuspid stenosis or atresia, tetralogy of fallot
- w/ isolated pulm stenosis, RV may be small or large
Ebstein anomaly
- malformation/malpositioning of tricuspid valve, displaced into RV
- leads to regurg & RA enlargement (large RA, small RV)
- poor prognosis - large heart, pulmonary hypoplasia, arrythmias
ASD/VSD/PDA
AV canal/Endocardial Cushion Defect
- large defect in central portion of heart
- involves both AV valves, atrial and ventricular septa
- poor prognosis
Tetralogy of Fallot
- Pulmonic stenosis (manifest as small PA), VSD, overriding aorta, RVH (first three seen in fetuses)
- prognosis good
Transposition of Great Vessels
- reversed ventricular outflow tracts
- dx best made on long axis LV view, both vessels extending cephalad in parallel, aorta anterior to PA
- often accompanied by VSD
- good prognosis
Truncus Arteriosis
- single large vessel arises from both ventricles giving branches to pulmonary, coronary, and systemic arteries
- associated L or R ventricular hypoplasia and a large VSD or AV canal
Cardiac Tumors
- most often rhabdomyomas, assoc w/ TS
- round or oval echogenic masses
Arrhythmias
- prognosis depends on presence of hydrops
- measured in M-mode
- tachycardia > 180-200bpm
- flutter > 300bpm
- a. fib > 400bpm
Ectopia cordis
- Heart located outside thorax
Pentalogy of Cantrell
- ectopia cordis & omphalocele
- also congenital cardiac defects, distal sternal cleft, ventral diaphragmatic hernia
OB - GI
Esophageal Atresia
- associated with VACTERL and TE fistula
- polyhydramnios
- if no distal TE fistula, no fluid in stomach
Duodenal Atresia
- “double bubble” & polyhydramnios
- ddx: annular pancreas, malro w/ Ladd's bands, duodenal web
Small Bowel Obstruction
- dilated bowel & polyhydramnios
- coffee bean = volvulus
Meconium Peritonitis
- peritoneal fluid or meconium pseudocyst
- may be thick-walled cyst with wall calcification
- later stages may have isolated intraperitoneal calcifications – calcifications exclude CF
- look for complex scrotal ascites
Omphalocele
- contains bowel and sometimes liver
- midline, covered by membrane
- cord vessels travel through it
- assoc w/ chromosomal anomalies
Gastroschisis
- paraumbilical, usually on right
- free-floating, not contained by membrane
- good prognosis
Amniotic Band Syndrome
- free edges of amnion adhere to fetus and entrap fetal parts
- amputation, abdominal/thoracic wall defects, facial clefts, encephaloceles
OB - GU
Renal Agenesis
- often associated GU anomalies, such as bicornuate uterus
- bilateral leads to oligohydramnios, causing a number of anomalies including pulmonary hypoplasia, abnormal facies, clubfeet (Potter syndrome)
Hydronephrosis (renal pelvis diameter dilatation)
- >4mm is dilated in first 23 wks, >7mm is dilated after 23 wks
- obstruction, VUR, prune belly
- level of obstruction (UPJ, UVJ, urethra)
- think of primary megaureter (aperistaltic distal ureteral segment
- posterior urethral valves causes bilateral hydro, large bladder & oligohydramnios; ddx urethral atresia
- can have urine ascites
Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney
- noncommunicating cysts of different sizes, replacing the parenchyma
- 40% unilateral; associated with contralateral anomalies
- caused by UPJ obstruction
- atrophies after birth
ARPKD
- enlarged echogenic kidneys (enlargement means > 4cm)
- may have hepatic fibrosis
- may see oligohydramnios and absent bladder in severe cases
Renal Ectopia
- pelvic, horseshoe, crossed-fused
Mesoblastic Nephroma
- solid, homogeneous mass
- indistinguishable from Wilms
Duplicated Coll System & Ectopic Ureterocele
Ovarian Cysts
- follicular cysts may occasionally develop due to placental or maternal hormones
Cloacal and Bladder Exstrophy
- lower anterior abdominal soft-tissue mass BELOW umbilicus
- sole finding may be nonvisualization of bladder
OB - MSK
Skleletal Dysplasias
- Thanatophoric dysplasia - shortening and bowing of long bones, narrow thorax, cloverleaf skull
- OI Type 2 - fractures, deformities of ribs and long bones, small thorax, poor mineralization of cranium and soft skull
- Achondrogenesis - extensive lack of ossification except for calvarium
- Hypophosphatasia - poor ossification and shortening of long bones
Skeletal Dysostoses
- Nager acrofacial dysostosis - upper extremities shortened w/ absence of one or more long bones and associated mandible and temporal bone anomalies
- PFFD - absence of proximal femur
Limb Amputations
- amniotic bands
Radial Ray Defects
- Cornelia de Lange, Fanconi, Holt-Oram, TAR, VATER
- associated with congenital heart defects and Trisomy 13 & 18
Polydactyly
- associated w/ short-rib polydactyly, chondroectodermal dysplasia, asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy, Meckel-Gruber and trisomy 13
Clinodactyly
- abnormal curvature of a finger, resulting in overlapping digits
- associated w/ trisomy 18 & 21
Clubfoot
- suspect when bones of foot are in same plane as tibia and fibula
- associated w/ other abnormalities (Trisomy 13 & 18)
Rockerbottom foot
- bottom of foot appears convex downward
- associated with skeletal dysplasias and trisomy 18
OB - Trisomies
Trisomy 13 (Patau)
- Holoprosencephaly
- Ventriculomegaly
- Microcephaly
- Agenesis of the corpus callosum
- Microphthalmia
- Hypotelorism
- Radial aplasia
- Polydactyly
- Flexion deformity of fingers
- Diaphragmatic defect (hernia/eventration)
- Omphalocele
- Cardiac anomalies
- Echogenic enlarged kidneys
Trisomy 18 (Edwards)
- Agenesis of the corpus callosum
- Choroid plexus cysts
- Hypoplastic cerebellum with enlarged cisterna magna
- Strawberry skull
- Two-vessel cord
- Micrognathia
- Hypotelorism
- Microphthalmia
- Clenched hand with overlapping index finger
- Clubfoot
- Rockerbottom foot
- Omphalocele
- Diaphragmatic hernia
- Cardiac anomalies
- Renal anomalies
- Intrauterine growth restriction
Trisomy 21 (Down)
- Cerebral ventriculomegaly
- Atrioventricular canal
- Ventricular septal defect
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Nuchal translucency > 2.2-2.8 mm at 11-14 weeks
- Nuchal fold 6 mm or greater at 16-20 weeks
- Duodenal atresia
Monosomy X (Turner)
- cystic hygromas/lymphangiectasia
- pleural effusions
- ascites
- horseshoe kidneys
Triploidy
- Common sonographic presentations - dead embryo or fetus w/ enlarged cystic placenta, severe early-onset growth restriction w/ enlarged cystic placenta
- Holoprosencephaly
- Dandy-Walker malformation
- Agenesis of the corpus callosum
- Micrognathia
- Microphthalmia
- Syndactyly of the third and forth fingers
- Clubfeet
- Omphalocele
- Cardiac anomalies
- Renal anomalies
Meckel-Gruber syndrome
- encephalocele
- polycystic kidneys
- polydactyly
- cleft palate
- cardiac anomalies
- liver cysts
- oligohydramnios
ob_gyn.txt · Last modified: 2024/09/03 18:13 by 192.168.0.1