pedi
Table of Contents
Pedi Neuro
External Hydrocephalus
- Benign extraaxial collections of infancy
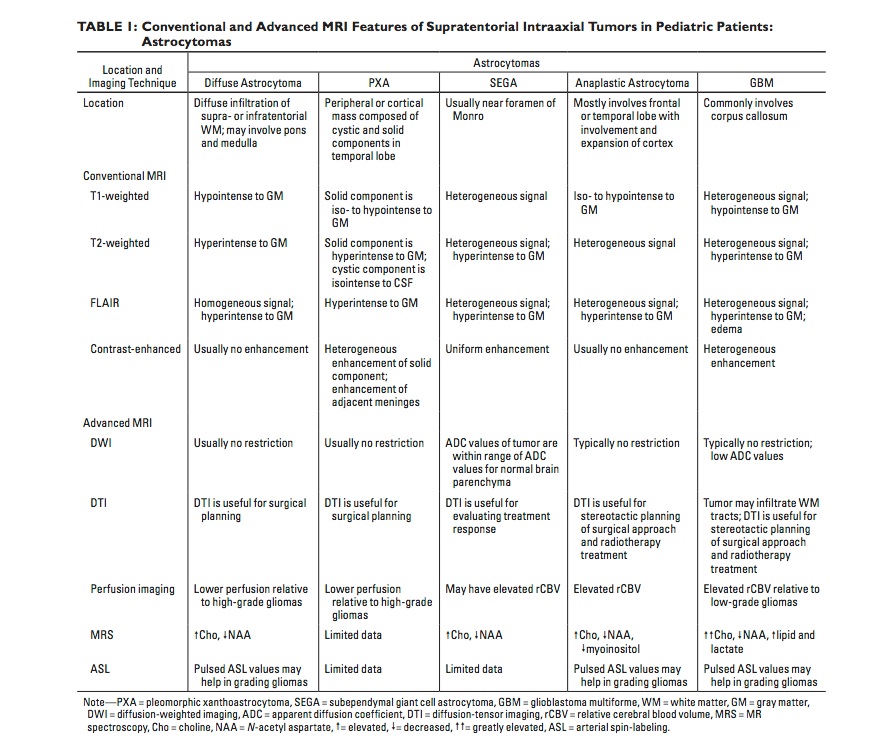
Cholesteatoma Types
- Primary/Congenital
- Epitympanum
- Secondary/Acquired
- Mesotympanum
Mineralizing Vasculopathy
- Branched-linear pattern of echogenicity in the region of the basal ganglia and thalami on echoencephalogram
- Follow the course of the lenticulostriate branches of the middle cerebral arteries
- Secondary to a cerebrovasculitic response to congenital infection (most often ascribed to rubella, CMV, and syphilis), anoxia, or rarely trisomy 13
DDx Scalp Fluid Collection
- Cephalohematoma
- Caput succedaneum
- Leptomeningeal cyst
- related to dural tear
- Subgaleal hematoma
DDx Stenosis @ Aqueduct Level
- Aqueductal stenosis
- Tectal glioma
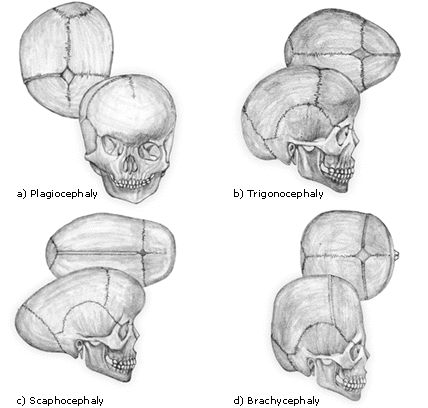
Craniosynostosis
- Scaphocephaly - Early fusion of the sagittal suture
- Anterior plagiocephaly - Early fusion of 1 coronal suture
- Brachycephaly - Early bilateral coronal suture fusion
- Posterior plagiocephaly - Early closure of 1 lambdoid suture
- Trigonocephaly - Early fusion of the metopic suture (metopic suture fuses between 6-8 months and sometimes as early as 3 months)
Pedi Cardiac
- Proper location for umbilical artery catheter = T8 - T12; alternative at L3 - L4
- Umbilical vein catheter tip should be at the right atrium
Pedi Cardiac DDx
| Acyanotic, normal vascularity | Acyanotic, increased vascularity | Cyanotic, decreased vascularity | Cyanotic, increased vascularity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aortic Stenosis | ASD (no LAE) | Tets (normal heart size, boot shaped) | TAPVR (Type 3 has nl heart size) |
| Pulmonic Stenosis | ECD (no LAE) | Ebstein | Transpostion |
| Coarctation | VSD | Pulmonic Atresia (w/ intact ventricular septum) | Truncus Arteriosis |
| Interrupted Aortic Arch | PDA | Tricuspid Atresia w/ PS | Tricuspid Atresia w/o PS |
| Cardiomyopathy/Pericardial Eff. | Single Ventricle/Double Outlet RV |
- I classify Pulmonic Atresia w/ VSD as a severe form of tetralogy
- Right Arch common w/ TGV, Truncus, Tets, Tricuspid Atresia (basically the cyanotic, increased vascularity ddx plus tets and minus TAPVR)
- Increased pulmonary flow, a right arch and cardiomegaly (biventricular) is classic for truncus arteriosus
- Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome has cardiomegaly, pulmonary edema, a small aorta, and is cyanotic
Cardiac Tumors in Children
- Rhabdomyoma (small, multiple)
- Fibroma
- Myxoma
Dilitation of Aortic Root
- Connective tissue disorders
- Takayasu's
- Syphilitic aortitis
- Neurofibromatosis
- FMD
- Giant cell arteritis
- Williams Syndrome
Tetralogy of Fallot
- Overriding Aorta
- VSD
- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
Types of TAPVR
- Type 1
- cardiomegaly and increased pulmonary vascularity
- widened mediastinum (“snowman heart”) due to vertical vein
- Type 2
- cardiomegaly and increased pulmonary vascularity
- simulates shunt physiology
- blood returns via pulmonary veins → coronary sinus → RA
- Type 3
- normal heart size, increased pulmonary vascularity
- blood returns via infradiaphragmatic systemic venous connection (IVC, hepatic vein, portal vein, etc.)
Newborn w/ CHF
- Aortic Anomalies
- aortic stenosis
- coarctation
- LV dysfxn
- aberrant L coronary artery
- myocarditis
- hypoplastic L heart syndrome
- Glycogen Storage Disease (Pompe)
- High Flow States
- vein of galen
- hemangioendothelioma
- anemia
- polycythemia
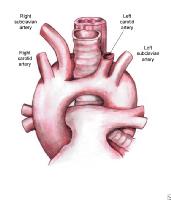
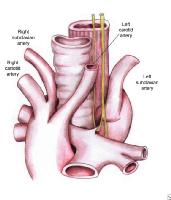
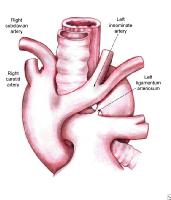
Most Common Vascular Rings
L Arch w/ Aberrant R Subclavian
- dysphagia lusoria
- low association w/ congenital heart disease
- not a true ring
Pedi Chest
Lung Lesions
Lucent
- CCAM (Type 1)
- CLE
- CDH
- PIE
Solid
- CCAM (Type 3)
- sequestration
- bronchgenic cyst
Complications of Cystic Fibrosis
- Recurrent Infections → Pseudomonas and Staph
- Lung Fibrosis
- Progressive Respiratory Failure
- Clubbing
- Pancreatic Insufficiency
- Liver Cirrhosis
- Rectal Prolapse
- Meconium Ileus, Meconium Peritonitis, Intussusception
- Sinusitis
- Infertility in Males
Hyperlucent Lung
- foreign body
- PTX
- congenital lobar emphysema
- most common LUL > RML > RUL
- pulmonary artery hypoplasia
- compensatory hyperinflation b/c of bad c/l lung
Neonatal Lung Infiltrates
| Surfactant Deficiency | TTN | Meconium Aspiration | Neonatal Pneumonia | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Patient | Preemie | Term/C-section | Post-term | PROM |
| Time Course | < 6 hrs | 24-48 hrs | 12-24 hrs | <6 hrs |
| Lung Volume | Decreased | Increased | Increased | Increased |
| Imaging | Ground-glass | Interstitial Edema | Coarse, Nodular, Asymmetric | Streaky, Perihilar |
TTN
- early (2-6 hr) prominent vascular markings with patchy round alveolar opacities and pleural fluid
- normal to large lung volumes, mild CM, rapid clearance by 42-78hrs, starting by 10-12hrs
RDS/HMD/Surfactant Deficiency
- Low lung volumes
- Ground-glass opacities
Meconium Aspiration
- patchy, bilateral, asymmetric coarse opacities, representing areas of SSA
- marked hyperaeration - 25% get PTX and pneumomediastinum
- CXR clearing takes several weeks & lags clinical improvement
- treatment is ECMO if severe
Neonatal PNA
- GBS looks like RDS, with bilateral granular, symmetric opacities and low lung volumes
- GBS usually has effusions and RDS rarely does
- other pneumonias resemble meconium aspiration, w/ patchy, asymmetric opacities and hyperaeration
- organisms - Group B Strep, CMV (viral pneumonitis), Chlamydia
Low Volume Pulmonary Opacification
- Pneumonia
- Hyaline Membrane Disease
- Neurogenic (Brain Damage)
DDx Retrocardiac Mass
- Neuroblastoma
- Sequestration
- Pneumonia
- Nerve Sheath Tumors
Tracheoesophageal Fistulas
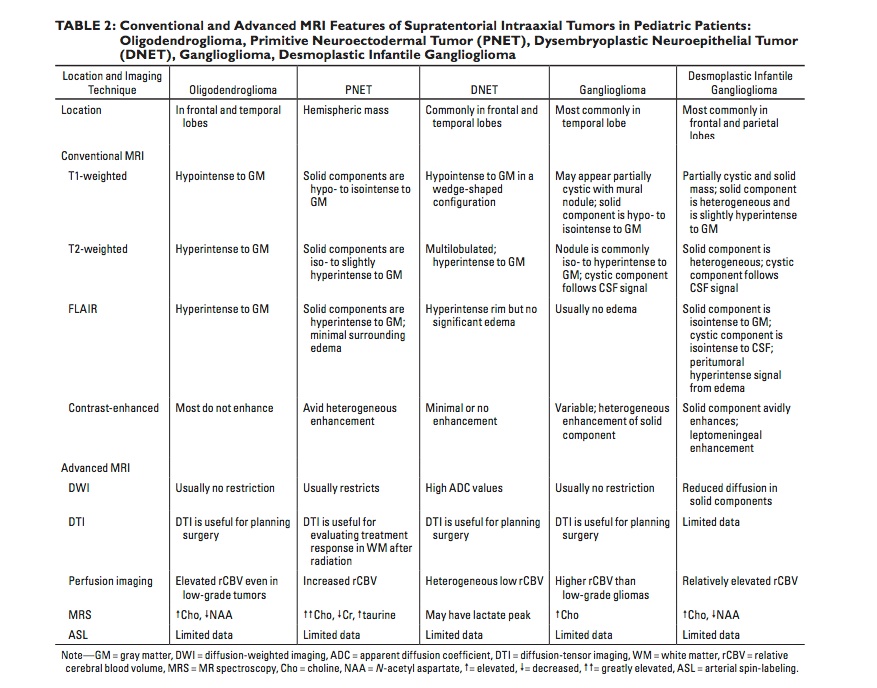
Pedi GI/GU
Normal Spleen Size
| Age | Spleen Length (cm) |
|---|---|
| 0-3 mo | <6 cm |
| 3-6 mo | <6.5 cm |
| 6-12 mo | <7 cm |
| 1-2 yr | <8 cm |
| 2-4 yr | <9 cm |
| 4-6 yr | <9.5 cm |
| 6-8 yr | <10 cm |
| 8-10 yr | <11 cm |
| 10-12 yr | <11.5 cm |
| 12-15 yr | <12 cm |
| 15-20 yr | <12 cm (female) |
| 15-20 yr | <13 cm (male) |
* Rosenberg, et.al. AJR 1991
Pediatric Liver Masses
<5 yr old
- hepatoblastoma
- most common primary malignant liver tumor of childhood, M > F, elevated AFP
- inhomogeneous appearance
- associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- hemangioendothelioma
- same CT appearance as adult hemangiomas; 50% calcify
- MR - low T1, very high T2, large flow voids, Gd enhancement like CT
- often presents w/ CHF or Kasabach-Meritt
- mesenchymal hamartoma
- large multilocular cystic mass with thin internal septations
- septa and any solid portions will enhance
- neuroblastoma mets
>5 yr old
- HCC
- mesenchymal sarcomas
- mets
- lymphoma
- adenoma
Abdominal Cyst
- Mesenteric Cyst
- Urachal Cyst
- Duplication Cyst
- Choledochal Cyst
- Abscess
- Hydronephrosis
- Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney
- Cystic Ovarian Mass
Bilateral Dilated Ureters
- Posterior Urethral Valves
- Prune-Belly Syndrome
- Bilateral Megaureter
Wilms vs Neuroblastoma
Mnemonics:
- Neuroblastoma encases and calcifies (NEC)
- Wilms invades and lung mets (WILM)
| Wilms | Neuroblastoma | |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Kidney | Adrenal or Sympathetic chain |
| Calcification | Uncommon (<15%) | Common (85%) |
| Appearance | Cystic/Solid | Solid |
| Vessels | Displaces & Invades | Encases |
| Mets | Lung | Early (bone, neural foramina, nodes) |
| Peak Age | 3 years | <2 years |
* Drash syndrome - Wilms, pseudohermaphroditism, glomerulonephritis
Neuroblastoma Staging
- 1 - confined to the organ of origin
- 2 - extension beyond the organ but not crossing midline
- 3 - extension across midline
- 4 - distal mets
- 4S - age <1 year, mets confined to skin, liver, and bone marrow (SLiM)
Wilms Staging
- 1 - confined to kidney, completely excised
- 2 - local extension, completely resected
- 3 - incomplete resection, no distant mets
- 4 - distant mets to lung, liver, bone, or brain
- 5 - bilateral synchronous tumors
Hypoperfusion Complex
- decreased calibur of aorta and IVC
- intense enhancement of bowel wall, aorta, IVC, pancreas, and kidneys
- dilated, fluid-filled bowel
- suggests tenuous hemodynamic state
Eagle-Barrett Syndrome
- abdominal wall muscle deficiency (“prune belly”)
- nonobstructed, but markedly dilated redundant ureters ± hydronephrosis ± renal dysplasia
- bilateral cryptorchidism
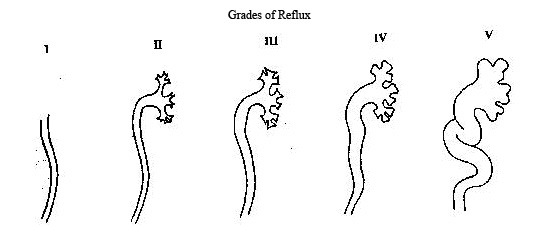
Vesicoureteral Reflux
- Grade I: Urine backs up into the ureter only, and the renal pelvis appears healthy, with sharp calyces.
- Grade II: Urine backs up into the ureter, renal pelvis, and calyces. The renal pelvis appears healthy and has sharp calyces.
- Grade III: Urine backs up into the ureter and collecting system. The ureter and pelvis appear mildly dilated, and the calyces are mildly blunted.
- Grade IV: Urine backs up into the ureter and collecting system. The ureter and pelvis appear moderately dilated, and the calyces are moderately blunted.
- Grade V: Urine backs up into the ureter and collecting system. The pelvis severely dilates, the ureter appears tortuous, and the calyces are severely blunted.
DDx Bladder Thickening
- hemorrhagic cystitis
- rhabdomyosarcoma
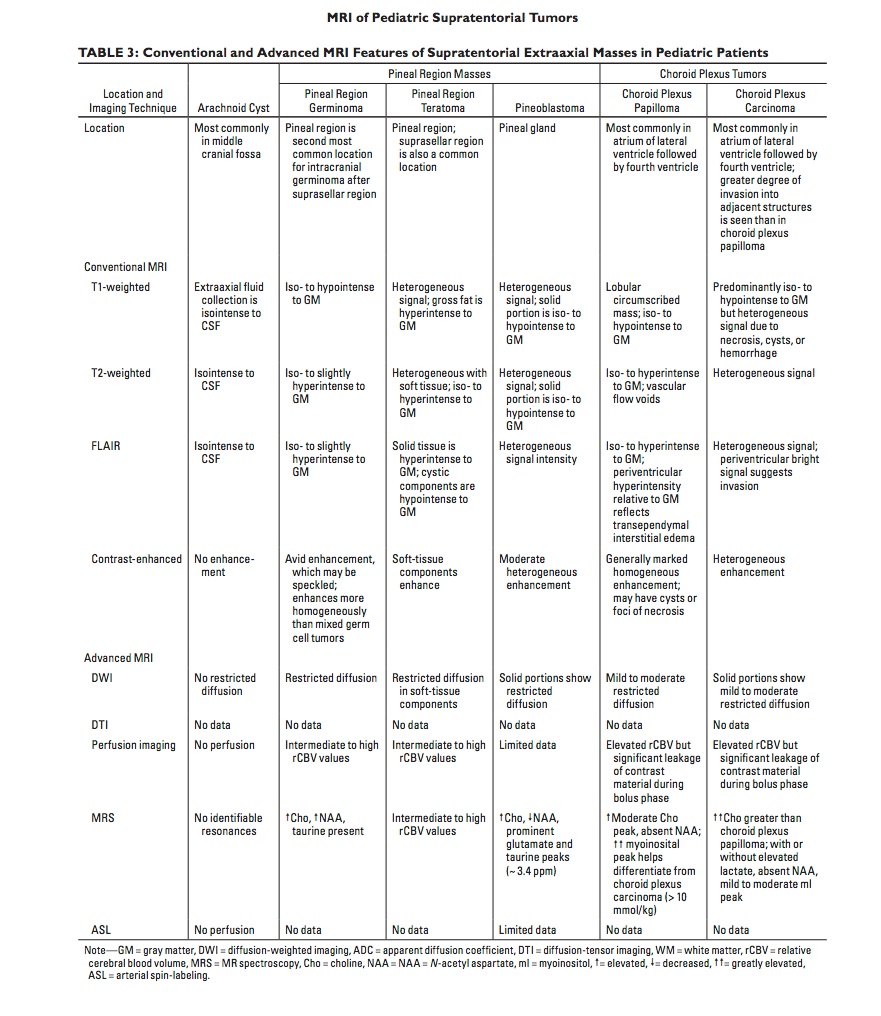
Pedi MSK
- Kohler's disease, if asymptomatic, is normal variant called Karp Dysplasia
- Blount's Disease = Tibia Vara
- The tarda form of hypophosphatasia mimics rickets radiographically
- Toddler's Fx - nondisplaced spiral fx of distal tibia
Scoliosis
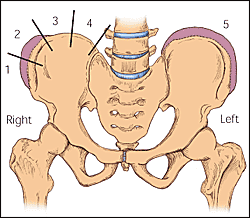
Risser Grades
- Ossification of the iliac apophysis starts at the anterior superior iliac spine and progresses posteromedially.
- The iliac crest is divided into quadrants, and the stage of maturity is designated as the number of ossified quadrants. For example, 50 percent ossified is a Risser grade 2. On the anatomic left (right side of the figure), all quadrants are ossified and the apophysis is fused to the iliac crest, for a Risser grade 5.
DDx
- Idiopathic (adolescent)
- usually females
- R thoracic ± L lumbar curve
- Juvenile (3-10 years)
- idiopathic
- 2:1 female predominance
- Infantile
- convex to L
- boys
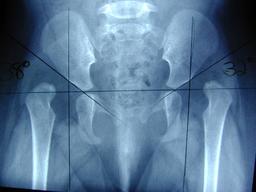
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
Risk Factors
- left hip is more often involved (? due to fetal positioning)
- females: 80% of cases
- breech birth (may account for 25-45% of DDH cases)
- first born
- fixed positions of extension and adduction
- Down's syndrome
Plain Film
- Hilgenreiner's line is drawn thru the triradiate cartilages
- Perkins line is perpendicular to that, drawn from the anterior inferior iliac spine
- Femoral head should be in the lower inner quadrant fromed by the lines
Ultrasound
- Alpha Angle
- measurement of acetabular concavity
- angle between the baseline and the roofline
- Beta Angle
- measured between the baseline and the inclination line
- indicates the acetabular cartilaginous roof coverage
- Type I hips
- alpha angle > 60°
- normal
- require no treatment and no follow-up
- Type II hips
- alpha angle = 50-59 degrees
- hip is normally located, but the bony acetabulum is immature
- if < 3mos → physiologic immaturity
- if > 3mos → mild dysplasia
- no treatment but should be closely observed clinically and with US until they meet type I criteria
- small risk of delayed displacement or acetabular dysplasia
- Type III hips (low displacement) and type IV hips (high displacement)
- beta angle < 55 degrees
- usually very apparent clinically
- both require immediate treatment
AVM of Hip
- causes coxa magna & coxa plana
Dense Metaphyseal Bands
- Lead Poisoning
- Heavy Metals
- Healing Phase of Rickets
Lucent Metaphyseal Bands
- Blue Cell Tumor (Ewings/Neuroblastoma)
- Leukemia/Lymphoma
- Ricketts
- Rubella
- Congenital Syphillis → Wimberger Sign
DDx Fragmented Epiphyses (HAMS)
- hypothyroidism
- delayed skeletal maturity (bone age more than 2 SD below the mean)
- small stature
- wormian bones
- enlarged sella
- fragmented epiphyses
- delayed closure of cranial sutures
- AVN (few epiphyses involved)
- multiple epiphyseal dysaplsia
- spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
DDx Metaphyseal Fraying (CHARMS)
- Congenital infections (Syphilis, CMV, Rubella)
- Hypophosphatasia
- Achondroplasia
- Ricketts
- Metaphyseal dysostosis
- Scurvy
DDx Erlenmeyer Flask (TOP DOG)
- Thalassemia (or other severe anemias)
- Osteopetrosis
- Pyle's disease (metaphyseal dysplasia)
- Diaphyseal aclasis (multiple osteochondromas)
- Ollier disease (multiple enchondromas)
- Gaucher disease
Mucopolysaccharidoses (Hunter/Hurler/Morquio)
- J-shaped Sella
- Dense Skull/Dense Bones
- Vertebral Body Beaking
- Canoe Paddle Ribs
- Basilar Invagination
- Dural Ectasia
- Proximal Metacarpal Tapering
Dwarfism
General
- Rhizomelic → proximal shortening (humerus or femur)
- Mesomelic → middle shortening (tibia/fibula or radius/ulna)
- Acromelic → distal shortening (hand)
- Micromelic → entire limb shortened
Achondroplasia
- Rhizomelic
- Increased craniofacial ratio
- Small skull base/foramen magnum
- Short vertebral bodies and large disc space
- Interpediculate distance decreases at more inferior levels in the L spine
- Pedicles are short and there is posterior vertebral body scalloping
- Metaphyses of long bones are flared
- Trident hand due to increased space between the middle fingers
- Iliac bones are short and rounded
- Decreased acetabular angles
- Champagne glass shaped true pelvis
- Lower extremities are short and thick
- Growth plates are “V” shaped
Thanatophoric
- Rhizomelic
- Severe platyspondyly, but with enlarged disc space, such that the overall thorax is nl in length
- Bowing and widening of femurs which look like telephone recievers
- Metaphyses are flared
- Small iliac wings and decreased acetabular angles
- May be a trident acetabulum
- Ribs are very short
- Tubular bones of the hands are feet and short and broad
- Interpediculate distance may be narrowed
- Cloverleaf skull
Jeune syndrome (asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy) and Ellis van Creveld
- Both are acromelic
- Very short ribs (especially Jeune) resulting in a very narrow chest, with a large appearing heart
- Trident acetabulum and decreased acetabular angle
- Premature ossification of the prox femoral epiphysis
- Skull and spine are normal, which helps distinguish from other dwarfisms
- Carpal bone fusions
- Polydactyly and an extra carpal bone are found much more commonly in ellis van creveld
- Could ask if the pt is Amish (ellis van creveld)
Camptomelic
- Main feature is bowing of the long bones of the lower extremity, with the apex pointing toward a skin dimple
- Also hypoplastic scapulae, small face vs skull, and dysplastic pelvic bones
Child Abuse
Suspicious Fractures for Child Abuse (MR SSS)
- Metaphyseal
- Rib
- Scapula
- Sternum
- Spinous process
Other Causes of Multiple Fxs
- osteogenesis imperfecta (look for osteopenia and wormian bones)
- neuromuscular disorders
- Menkes syndrome (also causes osteopenia and wormian bones plus WM hypomyelination, cerebral atrophy and subdural collections due to decreased copper absorption in GI tract)
- congenital insensitivity to pain
Periosteal Reaction
- physiologic/nl variant - should be only diaphyseal, smooth, symmetric, mostly along medial prox femur
- prostaglnadin txt
- Caffey’s
- neuroblastoma mets
- TORCH infections
- syphilis
Miscellaneous
Normal Umbilical Vein Catheter
- Goes from Umbilicus to Right Atrium
Normal Umbilical Artery Catheter
- Goes from Umbilicus to T6-10 or below L3
| Hemangioma | Lymphatic Malformations | Vascular Malformations |
|---|---|---|
| discrete masses | cystic, fluid-fluid levels | AV fistula, AVM |
| prominent enhancement | rim, septal, or no enhancement | capillary malformation |
| grow 1-2 years then involute | grows as child grows | venous malformation (may have calcification) |
Prostaglandin
- Keeps PDA Open
- Causes Mucosal Pyloric Hypertrophy
- Causes Periostitis
DDx for Thanatophoric Dwarf
- Jeune Syndrome (asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia)
- Homozygous Achondroplasia
DDx Wormian Bones (CHOP DIK)
- Cleidocranial Dysostosis
- Hypothyroidism/Hypophosphatasia
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- Pyknodysostosis/Progeria
- Down Syndrome
- Idiopathic
- Kinky Hair Syndrome
pedi.txt · Last modified: 2024/07/16 15:47 by 127.0.0.1